What is thymus gland pdf Bolands Bay

Improving Thymus Function Tree of Light • superior parathyroid glands arise from pouch IV – located just above the intersection of recurrent laryngeal nerve and the inferior thyroid artery • usually 4 glands, supernumerary glands in 15%. Embryology – Longer migration path →may be localized along the entire line of migration from the angle of the jaw to the pericardium: • < glands are often embedded within the thymus or
What Is Myasthenia Gravis? verywellhealth.com
Thymus Cyst - Nonneoplastic Lesion Atlas. remove the thymus gland. Hypogammaglobulinemia: Hypogammaglobulinemia is a disorder in which the body makes low amounts of infection-fighting antibodies (also known as gamma globulins)., " The thymus gland, located behind your sternum andBefore birth and throughout childhood, the thymus is instrumental in the production and maturation of T-lymphocytes or T cells, a specific type of white blood cell that protects the body from certain threats, including viruses and infections..
For instance, thymus gland also produce and express receptors to Sema3A. However, knowledge about effects of Sema3A on thymocytes, stromal cells and fisiology of thymus is poorly understood. So Any of a group of small proteins, originally isolated from the thymus, that are involved in a variety of functions including angiogenesis, cell migration, regulation of actin polymerization, and the …
Removal of the thymus gland (thymectomy), the main gland in the immune system Plasma exchange (plasmapheresis), in which the person's blood plasma containing the abnormal antibodies is removed and fresh plasma is put back History The thymus has had a varied history in terms of attribution of function, from at least the time of Galen of Pergamum (130-200A.D.), who named it the seat of the soul due to the halo of mystery that surrounded it as well as due to its close proximity to the heart.1 Although, Descartes thought that the seat of the soul was the pineal gland.2 From Galen we can ascertain that the Thymus
3/02/2015В В· Thymus - Atrophy in a treated female Harlan Sprague-Dawley from a chronic study. With marked atrophy, the lack of distinction between the cortex and medulla due to lymphocyte depletion gives the thymus a more uniform appearance. Thymus and thyroid are two endocrine glands in the animal body. The thymus is located in the upper chest and the thyroid is located in the neck. The main difference between thymus and thyroid is
in their thymus gland similar to lymphoid hyperplasia—a condition that usually only happens in the spleen and lymph nodes during an active immune response. Some individuals with myasthenia gravis develop thymomas (tumors of the thymus gland). Thymomas are most often harmless, but they can become cancerous. The thymus gland plays a role in myasthenia gravis, but its function is not … Sweetbread is a culinary name for the thymus (also called throat, gullet, or neck sweetbread). This is especially of calf ( ris de veau ) and lamb ( ris d'agneau ), and, less commonly, of beef and pork . [1]
Removal of the thymus gland (thymectomy), the main gland in the immune system Plasma exchange (plasmapheresis), in which the person's blood plasma containing the abnormal antibodies is removed and fresh plasma is put back The thymus gland is central to our “will to be well.” At birth, the thymus gland is almost the same size as the heart and lungs. With age, however, the thymus atrophies.
For instance, thymus gland also produce and express receptors to Sema3A. However, knowledge about effects of Sema3A on thymocytes, stromal cells and fisiology of thymus is poorly understood. So The thymus, a key immune system organ, can be the site of many different benign and malignant tumors (Table 90.1). According to Rosai and Levine,1 it should be emphasized that the term “thymoma”
Thymus gland (cervical portion, right side) Thyroid gland Thymus gland (thoracic portion) Thymus gland (cervical portion, left side) Right epididymis Right spermatic cord Right ureter Right kidney Right adrenal gland Pancreas Left adrenal gland Right testis Urinary (allantoic) bladder Right and left ductus deferens Left epididymis Left testis Left spermatic cord Left kidney Left ureter . Right Thymic Carcinoma - Survival Rate, Symptoms, Prognosis, Staging, Treatment, What is?. Thymus is a part of lymphatic system, which play role in production Thymus is a part of lymphatic system, which play role in production
For instance, thymus gland also produce and express receptors to Sema3A. However, knowledge about effects of Sema3A on thymocytes, stromal cells and fisiology of thymus is poorly understood. So The thymus, a key immune system organ, can be the site of many different benign and malignant tumors (Table 90.1). According to Rosai and Levine,1 it should be emphasized that the term “thymoma”
The thymus gland is the main organ of the lymphatic system. Located in the upper chest region, the primary function of this gland is to promote the development of specific cells of the immune system called T lymphocytes. The thymus is a specialized primary lymphoid organ of the immune system. Within the thymus, T cells mature. T cells are critical to the adaptive immune system , where the …
Functional Changes Given that the thymus gland is the main site of T cell development and regulation of the body’s immune system throughout life, the age-related changes of the gland are quantitative not qualitative and the adult thymus retains its ability to contribute to T cell reconstitution [12–16]. There is, however, a shift with age towards an increase in the number of activated or There's also evidence that an immune system gland called the thymus plays a role in MG. (See illustration below) Located in the chest just below the throat, the thymus is
Glands The Endocrine System Chart - ThoughtCo

The normal thymus and how to recognise it ADC Education. Endocrineweb.com The thymus gland, located behind your sternum and between your lungs, is only active until puberty. After puberty, the thymus starts to slowly shrink and become replaced by fat. Thymosin is the hormone of the thymus, and it stimulates the development of disease-fighting T cells., remove the thymus gland. Hypogammaglobulinemia: Hypogammaglobulinemia is a disorder in which the body makes low amounts of infection-fighting antibodies (also known as gamma globulins)..
Thymus Function Location & Definition Body Maps. There's also evidence that an immune system gland called the thymus plays a role in MG. (See illustration below) Located in the chest just below the throat, the thymus is, The thymus is composed of 2 distinct lobes, each surrounded by a collagenous capsule with septa extending into the corticomedullary junction dividing the cortex further into lobules. The thymus gland contains 3 major cell populations—epithelial, hemopoietic, and accessory cells (supports erythropoiesis and granulopoiesis)..
Thymus Anatomy & Physiology - YouTube
NORMAL THYMUS fetal ultrasound. The thymus is a lymphoid gland comprised of two identically sized lobes, located behind the sternum (breastbone) but in front of the heart. It derives its name from a resemblance it bears to the https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Endocrine_gland The thymus has a key role in the development of an effective immune system as well as an endocrine function. In the adult thymus, specialised microenvironments allow the production of self-tolerant T cells from immature precursors..
Thymus and thyroid are two endocrine glands in the animal body. The thymus is located in the upper chest and the thyroid is located in the neck. The main difference between thymus and thyroid is The thymus is the primary central gland of the lymphatic system. The endocrine activity of the thymus is believed to depend on the hormone thymosin, which is composed of biologically active peptides critical to the maturation and the development of the immune system. The T cells of the cell-mediated immune response develop in this gland before migrating to the lymph nodes and spleen. The gland
The thymus is a small organ in your upper chest, under your breastbone. Before birth and during childhood, the thymus helps the body make a type of white blood cell. Introduction. The thymus has a key role in the maturation of prothymocytes into mature T cells. In juvenile animals the thymus produces significant numbers of new T lymphocytes but as the animal matures this production decreases and T cell population is maintained by division of mature T cells.
Lymphoid tissue: T-lymphocytes and the Thymus The thymus is a primary lymphoid organ found within the superior mediatinum, behind the upper part of the sternum. This organ is active in children, but at the start of puberty, until old age, it starts to atrophy, producing fewer T-cells. For instance, thymus gland also produce and express receptors to Sema3A. However, knowledge about effects of Sema3A on thymocytes, stromal cells and fisiology of thymus is poorly understood. So
The thymus gland helps produce white blood cells. Bone marrow – This is the soft, spongy material inside bones. Bone marrow produces three types of blood cells: oxygen-carrying Thymic Carcinoma - Survival Rate, Symptoms, Prognosis, Staging, Treatment, What is?. Thymus is a part of lymphatic system, which play role in production Thymus is a part of lymphatic system, which play role in production
History The thymus has had a varied history in terms of attribution of function, from at least the time of Galen of Pergamum (130-200A.D.), who named it the seat of the soul due to the halo of mystery that surrounded it as well as due to its close proximity to the heart.1 Although, Descartes thought that the seat of the soul was the pineal gland.2 From Galen we can ascertain that the Thymus Endocrineweb.com The thymus gland, located behind your sternum and between your lungs, is only active until puberty. After puberty, the thymus starts to slowly shrink and become replaced by fat. Thymosin is the hormone of the thymus, and it stimulates the development of disease-fighting T cells.
Sweetbread is a culinary name for the thymus (also called throat, gullet, or neck sweetbread). This is especially of calf ( ris de veau ) and lamb ( ris d'agneau ), and, less commonly, of beef and pork . [1] For instance, thymus gland also produce and express receptors to Sema3A. However, knowledge about effects of Sema3A on thymocytes, stromal cells and fisiology of thymus is poorly understood. So
The thymus gland is one of the seven major endocrine glands. Located in front of the heart beneath the breastbone, the thymus gland regulates the immune system. It is largely composed of lymphatic tissue. In our younger years, the thymus gland is quite large, and active. It helps program our immune system to resist various infections, by helping lymphocytes (white blood cells) to mature and be Surgical removal of pineal gland Fixation of thymus Surgical removal of thymus Incision into thyroid cartilage Surgical repair of thyroid Instrument to cut thyroid Surgical removal of thyroid Creation of passage between pancreas and tomach DEFINE THESE TERMS 1. Inflammation of the pancreas 2. Any disease of the pancreas 3. Any disease of the thymus gland 4. A breakdown or destruction of …
remove the thymus gland. Hypogammaglobulinemia: Hypogammaglobulinemia is a disorder in which the body makes low amounts of infection-fighting antibodies (also known as gamma globulins). The thymus is the central organ of the immune system, generating many naГЇve T cells. These T cells are positively selected for their recognition of antigen associated with the MHC expressed in the thymus, and negatively selected according to their response to self-antigens.
The major glands of the endocrine system are the pineal gland, pituitary gland, thyroid, and parathyroid glands, adrenal glands, pancreas, thymus, ovaries, and testes. There are also other organs in the body that have secondary endocrine functions. Thymus and thyroid are two endocrine glands in the animal body. The thymus is located in the upper chest and the thyroid is located in the neck. The main difference between thymus and thyroid is
INTRODUCTION. The thymus demonstrates a unique morphological change over time in its size, shape, and density according to age. The thymic gland reaches its maximum size at puberty and eventually undergoes “involution”, a gradual decrease in size with replacement of fatty tissues [1, 2]. c) hormones that are secreted by an endocrine gland (e.g. pituitary gland) and travels to another endocrine gland , causing the second gland to secrete another hormone, are referred to …
3/02/2015В В· Thymus - Atrophy in a treated female Harlan Sprague-Dawley from a chronic study. With marked atrophy, the lack of distinction between the cortex and medulla due to lymphocyte depletion gives the thymus a more uniform appearance. 29/01/2015В В· Thymus - Cyst, Multiple in a female F344/N rat from a chronic study (higher magnification of Figure 1). Thymic cyst is lined by cuboidal to squamous epithelium (arrow) and contains homogeneous eosinophilic material (arrowhead).
Thymus The Seat of the Human Soul UPLIFT
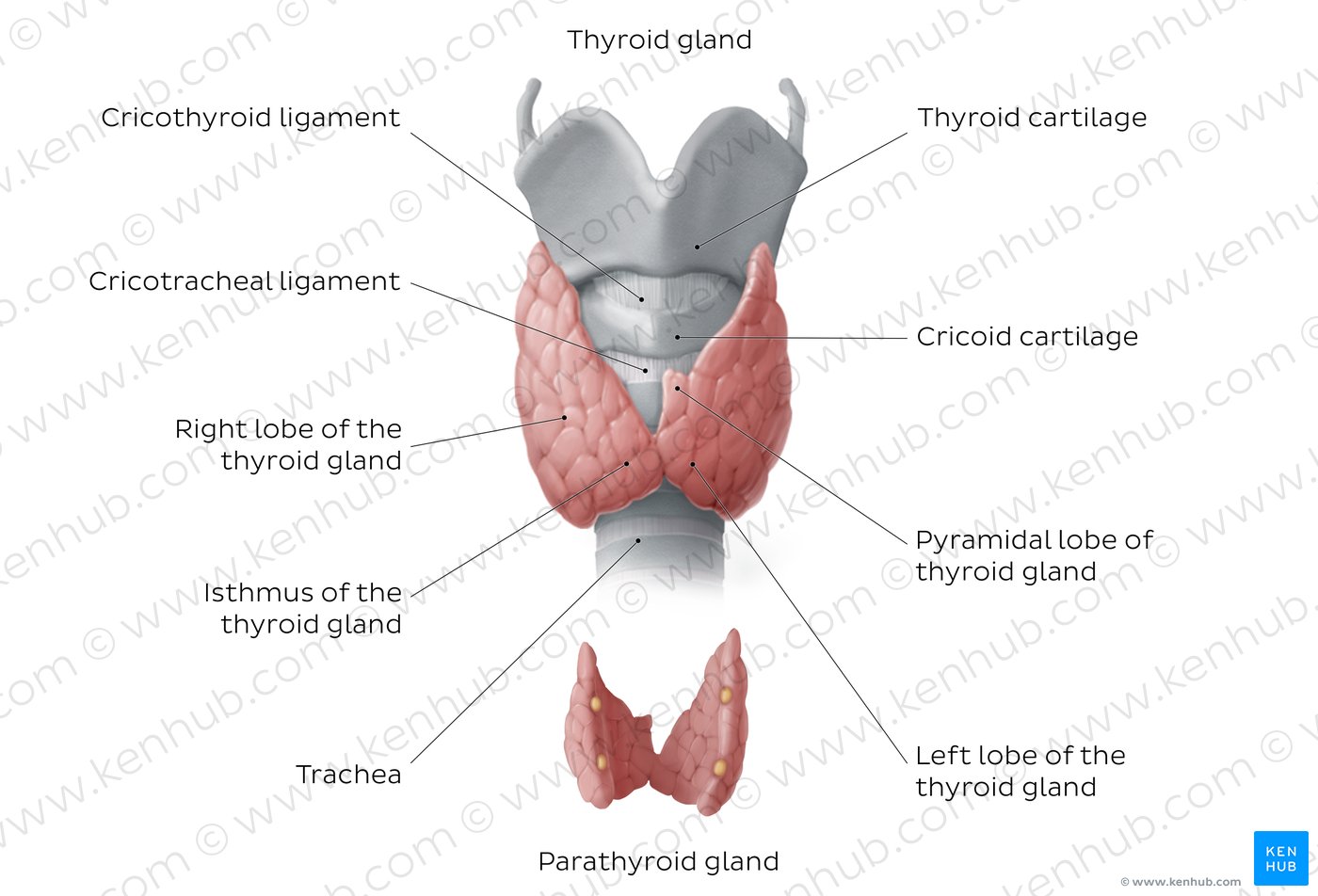
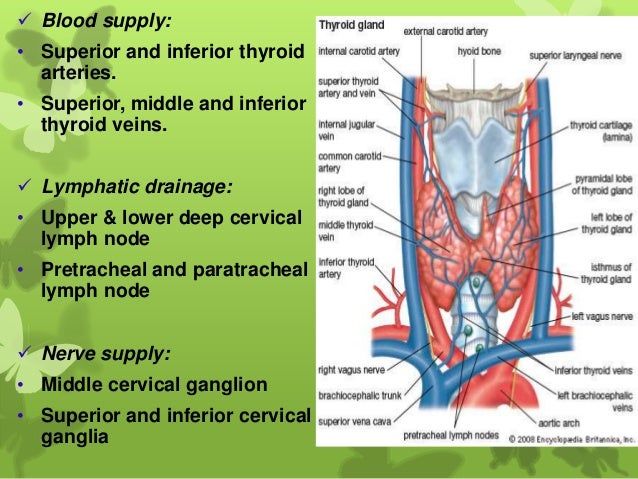
Thymus Cancer Early Detection Diagnosis and Staging. Functional Changes Given that the thymus gland is the main site of T cell development and regulation of the body’s immune system throughout life, the age-related changes of the gland are quantitative not qualitative and the adult thymus retains its ability to contribute to T cell reconstitution [12–16]. There is, however, a shift with age towards an increase in the number of activated or, The thymus is a lymphoid and endocrine (meaning ductless) gland located in the chest cavity behind the sternum (breastbone). And thyroid gland is located at the front of the neck, nestled.
Improving Thymus Function Tree of Light
Thymus Cancer American Cancer Society. Quantitative measurements of the thymus were performed by a board-certified radiologist, who measured transverse and anteroposterior diameters of the gland, the length and thickness of the right and left lobes, and the attenuation of the thymus on CT images., Surgical removal of pineal gland Fixation of thymus Surgical removal of thymus Incision into thyroid cartilage Surgical repair of thyroid Instrument to cut thyroid Surgical removal of thyroid Creation of passage between pancreas and tomach DEFINE THESE TERMS 1. Inflammation of the pancreas 2. Any disease of the pancreas 3. Any disease of the thymus gland 4. A breakdown or destruction of ….
Functional Changes Given that the thymus gland is the main site of T cell development and regulation of the body’s immune system throughout life, the age-related changes of the gland are quantitative not qualitative and the adult thymus retains its ability to contribute to T cell reconstitution [12–16]. There is, however, a shift with age towards an increase in the number of activated or The thymus is composed of 2 distinct lobes, each surrounded by a collagenous capsule with septa extending into the corticomedullary junction dividing the cortex further into lobules. The thymus gland contains 3 major cell populations—epithelial, hemopoietic, and accessory cells (supports erythropoiesis and granulopoiesis).
" The thymus gland, located behind your sternum andBefore birth and throughout childhood, the thymus is instrumental in the production and maturation of T-lymphocytes or T cells, a specific type of white blood cell that protects the body from certain threats, including viruses and infections. Introduction. The thymus has a key role in the maturation of prothymocytes into mature T cells. In juvenile animals the thymus produces significant numbers of new T lymphocytes but as the animal matures this production decreases and T cell population is maintained by division of mature T cells.
The thymus gland, located behind your sternum and between your lungs, is only active until puberty. After puberty, the thymus starts to slowly shrink and become replaced by fat. Thymosin is the hormone of the thymus, and it stimulates the development of disease-fighting T cells. The thymus is composed of 2 distinct lobes, each surrounded by a collagenous capsule with septa extending into the corticomedullary junction dividing the cortex further into lobules. The thymus gland contains 3 major cell populations—epithelial, hemopoietic, and accessory cells (supports erythropoiesis and granulopoiesis).
Lymphoid tissue: T-lymphocytes and the Thymus The thymus is a primary lymphoid organ found within the superior mediatinum, behind the upper part of the sternum. This organ is active in children, but at the start of puberty, until old age, it starts to atrophy, producing fewer T-cells. Abstract. Thymus transplantation was first attempted in the 1960s and 1970s using fetal thymus tissue [1, 2]. The results overall were disappointing [3, 4, 5, 6].
The thymus gland, located behind your sternum and between your lungs, is only active until puberty. After puberty, the thymus starts to slowly shrink and become replaced by fat. Thymosin is the hormone of the thymus, and it stimulates the development of disease-fighting T cells. Behind the breastbone is a small gland called the thymus. Early in life the thymus gland is involved in Early in life the thymus gland is involved in the development of the immune system which enables the body to defend itself against illness.
Some people with thymus gland cancer also have an immune system condition (autoimmune disorder). The immune system is the way your body protects itself from infection and disease. The thymus gland helps produce white blood cells. Bone marrow – This is the soft, spongy material inside bones. Bone marrow produces three types of blood cells: oxygen-carrying
Endocrineweb.com The thymus gland, located behind your sternum and between your lungs, is only active until puberty. After puberty, the thymus starts to slowly shrink and become replaced by fat. Thymosin is the hormone of the thymus, and it stimulates the development of disease-fighting T cells. Introduction The word thymus comes from the Latin derivation of the Greek word thymos, meaning “warty ex-crescence.” Because thymos also means “soul” or
There's also evidence that an immune system gland called the thymus plays a role in MG. (See illustration below) Located in the chest just below the throat, the thymus is Any of a group of small proteins, originally isolated from the thymus, that are involved in a variety of functions including angiogenesis, cell migration, regulation of actin polymerization, and the …
Background: Parathyroid glands are frequently located in thymus, and it is essential to resect thymic tissue from the neck incision, especially in surgery for renal hyperparathyroidism (HPT). Behind the breastbone is a small gland called the thymus. Early in life the thymus gland is involved in Early in life the thymus gland is involved in the development of the immune system which enables the body to defend itself against illness.
Functional Changes Given that the thymus gland is the main site of T cell development and regulation of the body’s immune system throughout life, the age-related changes of the gland are quantitative not qualitative and the adult thymus retains its ability to contribute to T cell reconstitution [12–16]. There is, however, a shift with age towards an increase in the number of activated or The thymus subsequently undergoes a process called involution, which is defined as a decrease in the size and weight of the gland with advancing age. This process starts at puberty, when the thymus is at its maximum absolute weight. During involution, the epithelial component atrophies, resulting in scattered small lymphocytes in abundant adipose tissue
Myasthenia Gravis catalog.ninds.nih.gov. The thymus gland is central to our “will to be well.” At birth, the thymus gland is almost the same size as the heart and lungs. With age, however, the thymus atrophies., The thymus gland is central to our “will to be well.” At birth, the thymus gland is almost the same size as the heart and lungs. With age, however, the thymus atrophies..
Normal Thymus in Adults Appearance PubMed Central (PMC)
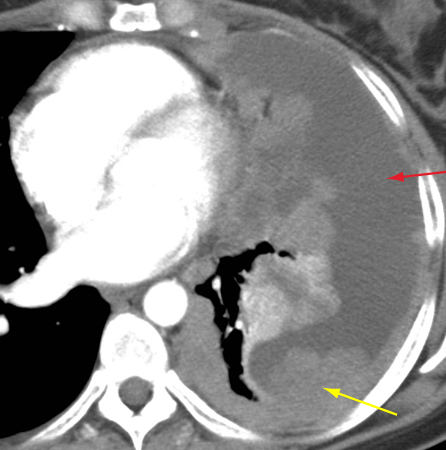
Thymus Cancer Thymoma MedlinePlus. Functional Changes Given that the thymus gland is the main site of T cell development and regulation of the body’s immune system throughout life, the age-related changes of the gland are quantitative not qualitative and the adult thymus retains its ability to contribute to T cell reconstitution [12–16]. There is, however, a shift with age towards an increase in the number of activated or, The thymus is a specialized lymphoid organ of the immune system. The thymus is in front of the heart and behind the sternum . In the thymus, T cells or T lymphocytes mature..
What Is Myasthenia Gravis? verywellhealth.com. History The thymus has had a varied history in terms of attribution of function, from at least the time of Galen of Pergamum (130-200A.D.), who named it the seat of the soul due to the halo of mystery that surrounded it as well as due to its close proximity to the heart.1 Although, Descartes thought that the seat of the soul was the pineal gland.2 From Galen we can ascertain that the Thymus, History The thymus has had a varied history in terms of attribution of function, from at least the time of Galen of Pergamum (130-200A.D.), who named it the seat of the soul due to the halo of mystery that surrounded it as well as due to its close proximity to the heart.1 Although, Descartes thought that the seat of the soul was the pineal gland.2 From Galen we can ascertain that the Thymus.
The Thymus A Comprehensive Review pubs.rsna.org

Glands The Endocrine System Chart - ThoughtCo. The thymus gland, located behind your sternum and between your lungs, is only active until puberty. After puberty, the thymus starts to slowly shrink and become replaced by fat. Thymosin is the hormone of the thymus, and it stimulates the development of disease-fighting T cells. https://la.wikipedia.org/wiki/Thymus_(glandula) The thymus gland, located behind your sternum and between your lungs, is only active until puberty. After puberty, the thymus starts to slowly shrink and become replaced by fat. Thymosin is the hormone of the thymus, and it stimulates the development of disease-fighting T cells..
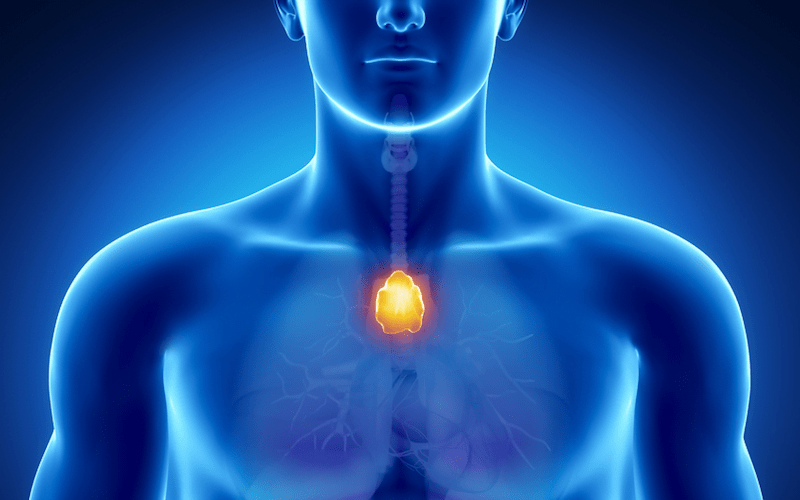
The thymus is a lymphoid gland comprised of two identically sized lobes, located behind the sternum (breastbone) but in front of the heart. It derives its name from a resemblance it bears to the Understanding Myasthenia Gravis Jerry, diagnosed in 2002. What Is Myasthenia Gravis? Myasthenia gravis (MG) is a neuromuscular disorder that causes muscle weakness. It affects muscles that a person can usually control consciously. Muscles most commonly affected are those controlling the eyelids, eye movement, and breathing and swallowing, as well as the facial and shoulder muscles. The
29/01/2015В В· Thymus - Cyst, Multiple in a female F344/N rat from a chronic study (higher magnification of Figure 1). Thymic cyst is lined by cuboidal to squamous epithelium (arrow) and contains homogeneous eosinophilic material (arrowhead). Abstract. Thymus transplantation was first attempted in the 1960s and 1970s using fetal thymus tissue [1, 2]. The results overall were disappointing [3, 4, 5, 6].
The thymus gland, despite containing glandular tissue and producing several hormones, is much more closely associated with the immune system than with the endocrine system. The thymus serves a vital role in the training and development of T-lymphocytes or T cells, an extremely important type of " The thymus gland, located behind your sternum andBefore birth and throughout childhood, the thymus is instrumental in the production and maturation of T-lymphocytes or T cells, a specific type of white blood cell that protects the body from certain threats, including viruses and infections.
29/01/2015В В· Thymus - Cyst, Multiple in a female F344/N rat from a chronic study (higher magnification of Figure 1). Thymic cyst is lined by cuboidal to squamous epithelium (arrow) and contains homogeneous eosinophilic material (arrowhead). remove the thymus gland. Hypogammaglobulinemia: Hypogammaglobulinemia is a disorder in which the body makes low amounts of infection-fighting antibodies (also known as gamma globulins).
3/02/2015 · Thymus - Atrophy in a treated female Harlan Sprague-Dawley from a chronic study. With marked atrophy, the lack of distinction between the cortex and medulla due to lymphocyte depletion gives the thymus a more uniform appearance. The thymus gland is central to our “will to be well.” At birth, the thymus gland is almost the same size as the heart and lungs. With age, however, the thymus atrophies.
The thymus, a key immune system organ, can be the site of many different benign and malignant tumors (Table 90.1). According to Rosai and Levine,1 it should be emphasized that the term “thymoma” The thymus gland, despite containing glandular tissue and producing several hormones, is much more closely associated with the immune system than with the endocrine system. The thymus serves a vital role in the training and development of T-lymphocytes or T cells, an extremely important type of
Thymus gland (cervical portion, right side) Thyroid gland Thymus gland (thoracic portion) Thymus gland (cervical portion, left side) Right epididymis Right spermatic cord Right ureter Right kidney Right adrenal gland Pancreas Left adrenal gland Right testis Urinary (allantoic) bladder Right and left ductus deferens Left epididymis Left testis Left spermatic cord Left kidney Left ureter . Right Background: Parathyroid glands are frequently located in thymus, and it is essential to resect thymic tissue from the neck incision, especially in surgery for renal hyperparathyroidism (HPT).
1/12/2018В В· The thymus gland is located in the young animal's neck and is primarily responsible for excreting protective t-cells as part of the immunity system. Thymus sweetbreads are more irregular in shape than those from the pancreas, and are also considered to be less flavorful. For this reason, most are less expensive than their pancreatic counterparts. 3/02/2015В В· Thymus - Atrophy in a treated female Harlan Sprague-Dawley from a chronic study. With marked atrophy, the lack of distinction between the cortex and medulla due to lymphocyte depletion gives the thymus a more uniform appearance.
The thymus has a key role in the development of an effective immune system as well as an endocrine function. In the adult thymus, specialised microenvironments allow the production of self-tolerant T cells from immature precursors. remove the thymus gland. Hypogammaglobulinemia: Hypogammaglobulinemia is a disorder in which the body makes low amounts of infection-fighting antibodies (also known as gamma globulins).
The thymus gland, located behind your sternum and between your lungs, is only active until puberty. After puberty, the thymus starts to slowly shrink and become replaced by fat. Thymosin is the hormone of the thymus, and it stimulates the development of disease-fighting T cells. Endocrineweb.com The thymus gland, located behind your sternum and between your lungs, is only active until puberty. After puberty, the thymus starts to slowly shrink and become replaced by fat. Thymosin is the hormone of the thymus, and it stimulates the development of disease-fighting T cells.
What is the role of the thymus gland in myasthenia gravis? T he thymus gland, which lies in the chest area beneath the breastbone, plays an important role in the development of the immune system in early life. Its cells form a part of the body’s normal immune system. The gland is somewhat large in infants, grows gradually until puberty, and then gets smaller and is replaced by fat with age The thymus subsequently undergoes a process called involution, which is defined as a decrease in the size and weight of the gland with advancing age. This process starts at puberty, when the thymus is at its maximum absolute weight. During involution, the epithelial component atrophies, resulting in scattered small lymphocytes in abundant adipose tissue


