Lte physical layer tutorial pdf Manitowaning

LTE and WiMAX Comparison Semantic Scholar Long Term Evolution (LTE) - A Tutorial Ahmed Hamza aah10@cs.sfu.ca Network Systems Laboratory Simon Fraser University October 13, 2009 Ahmed Hamza Long Term Evolution (LTE) - A Tutorial October 13, 2009 1 / 48
LTE Tutorial Physical Channel Structure
Long Term Evolution (LTE) A Tutorial. 7 26.01.2002 WCDMA Physical Layer Channelisation (2/3) • In the uplink, it can only separate the physical channels/services of one user because the mobiles are not synchronised in time., LTE defines a number of downlink physical channels to carry information blocks received from the MAC and higher layers. These channels are categorized as transport or control channels. These channels are categorized as transport or control channels..
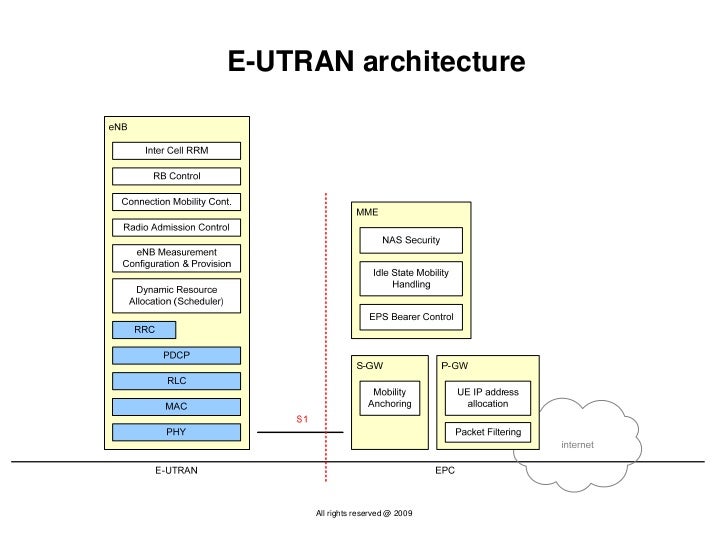
Overview of the LTE physical layer--Part I in Tutorial , LTE physical layer , LTE Telesystem Innovations - This article presents an overview of the LTE physical layer with a focus on essential aspects of the physical layer for FDD mode, which is the dominant mode of operation. Below is a logical digram of E-UTRAN Protocol layers with a depiction of data flow through various layers: Packets received by a layer are called Service Data Unit (SDU) while the packet output of a layer is referred to by Protocol Data Unit (PDU).
LTE improves spectrum efficiency, also defined relative to Release 6. The downlink target is three to four times the The downlink target is three to four times the spectral efficiency of High-Speed Downlink Packet Access (HSDPA) while the uplink target is a two to three time Long Term Evolution (LTE) - A Tutorial Ahmed Hamza aah10@cs.sfu.ca Network Systems Laboratory Simon Fraser University October 13, 2009 Ahmed Hamza Long Term Evolution (LTE) - A Tutorial October 13, 2009 1 / 48
LTE Physical Layer. LTE Physical Layer . is 10*log 10 (Total no.RS EPRE and RSRP RS power per subcarrier and symbol Two of the subcarriers in selected symbols in each Resource Block are used for RS from each transmitter.Power Levels .RSRPDiff -85 = TxPowerLevel To Be Set .7 . called Energy per Resource Element (EPRE) in the standard. SC-FDMA & OFDMA in LTE physical layer Murtadha Ali Nsaif Sukar #1 and Maninder Pal *2 #1M.Tech Scholar,Department of Electronics & Communication Engineering,
www.rfwireless-world.com Basics of LTE System Introduction: Third-generation (3G) wireless systems, based on W-CDMA, are now being deployed all over the world. www.rfwireless-world.com Basics of LTE System Introduction: Third-generation (3G) wireless systems, based on W-CDMA, are now being deployed all over the world.
EventHelix.com •telecommunication design •systems engineering •real-time and embedded systems LTE Channel Architecture PHY Physical Channels MAC EventHelix.com •telecommunication design •systems engineering •real-time and embedded systems LTE Channel Architecture PHY Physical Channels MAC
LTE-Sim is an open source framework to simulate LTE networks. It encompasses several aspects of LTE networks, including both the Evolved Universal Terrestrial Radio Access (E-UTRAN) and the Evolved Packet System (EPS). – Physical layer defined – Upper layers specifications defined are stable enough for implementation – Most of service layer and security adopted from the existing MBMS spec
7 26.01.2002 WCDMA Physical Layer Channelisation (2/3) • In the uplink, it can only separate the physical channels/services of one user because the mobiles are not synchronised in time. EventHelix.com •telecommunication design •systems engineering •real-time and embedded systems LTE Channel Architecture PHY Physical Channels MAC
Short, informal videos on the hottest LTE topics by our team of Subject Matter Experts (SMEs) Outline of the talk Brief overview of the eNodeB MAC-PHY interface Information sent by the MAC to the PHY oData and control information Concepts of Adaptive Modulation & Coding, BLER &
A COMPREHENSIVE ANALYSIS OF LTE PHYSICAL LAYER by Fahimeh Rezaei A THESIS Presented to the Faculty of The Graduate College at the University of Nebraska In Partial Fulfillment of Requirements For the Degree of Master of Science Major: Telecommunications Engineering Under the Supervision of Professor Hamid.R Sharif-Kashani Lincoln, Nebraska December, 2010 . A COMPREHENSIVE ANALYSIS OF THE LTE 3glteinfo FREE LTE tutorials and training to get basic and in depth knowledge on various 3GPP Long Term Evolution protocols and procedures. If you are just starting with 3GPP LTE or you have some experience with wireless technologies, our LTE tutorials will help you to understand the next big thing on mobile evolution.
Below is a logical digram of E-UTRAN Protocol layers with a depiction of data flow through various layers: Packets received by a layer are called Service Data Unit (SDU) while the packet output of a layer is referred to by Protocol Data Unit (PDU). Downlink Channel Mapping 1 MIB SIB 4 3 2 Source: Erik Dahlman, Stefan Parkvall, and Johan Skold. 2013. 4G: LTE/LTE-Advanced for Mobile Broadband (2nd ed.).
Physical Channel Structure. The following list describes LTE downlink physical channels and physical signals. Downlink physical channels carry layer 2 information but downlink physical signals are only used by the physical layer. LTE-Sim is an open source framework to simulate LTE networks. It encompasses several aspects of LTE networks, including both the Evolved Universal Terrestrial Radio Access (E-UTRAN) and the Evolved Packet System (EPS).
LTE Protocol Stack YouTube
Long Term Evolution (LTE) A Tutorial. LTE video tutorials @RohdeSchwarz presentations provide an excellent introduction to LTE. The presentations are accompanied with an audio narration., Abstract: Physical layer control signals in cellular communications serve the purpose of delivering physical layer control messages in a timely fashion to support cell radio resource management and data transmissions between the network and the mobile users..
Introduction to the LTE Physical Layer Meetup
Introduction to LTE Physical Layer Video Tutorials. – Specific Channel and PHY layer models for LTE macro and small cells • An Open source simulator: • UE has to report a set of measurements of the eNBs when it receives their physical cell identity (PCI) – reference signal received power (RSRP) ~ “average” power across the RBs – reference signal received quality (RSRQ) ~ “average” ratio between the power of the cell and Physical Interface. 3GPP describes LTE radio access technology is described as follows: The multiple access scheme for the LTE physical layer is based on Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiple Access (OFDMA) with a Cyclic Prefix (CP) in the downlink and a Single Carrier Frequency Division Multiple Access (SC-FDMA) with CP in the uplink..

LTE Physical Layer Overview. There are two types of frame structure in the LTE standard, Type 1 and Type 2. Type 1 uses Frequency Division Duplexing (uplink and downlink separated by frequency), and TDD uses Time Division Duplexing (uplink and downlink separated in time). The LTE physical layer is unique because it has asymmetrical modulation and data rates for uplink and downlink. The standard is designed for full-duplex operation, with simultaneous transmission and reception. The radio is optimized for performance on the downlink, because the transmitter at the base station has plenty of power. On the uplink, the radio is optimized more for power consumption
Physical layer control signals in cellular communications serve the purpose of delivering physical layer control messages in a timely fashion to support cell radio The LTE physical layer is unique because it has asymmetrical modulation and data rates for uplink and downlink. The standard is designed for full-duplex operation, with simultaneous transmission and reception. The radio is optimized for performance on the downlink, because the transmitter at the base station has plenty of power. On the uplink, the radio is optimized more for power consumption
"lte physical layer" courses, certification and training IoT Internet of Things Online self paced certification This covers the growth of internet of things encompassing devices for actuation, communication, sensing and processing to develop knowledge and experience in … Below is a logical digram of E-UTRAN Protocol layers with a depiction of data flow through various layers: Packets received by a layer are called Service Data Unit (SDU) while the packet output of a layer is referred to by Protocol Data Unit (PDU).
LTE improves spectrum efficiency, also defined relative to Release 6. The downlink target is three to four times the The downlink target is three to four times the spectral efficiency of High-Speed Downlink Packet Access (HSDPA) while the uplink target is a two to three time A COMPREHENSIVE ANALYSIS OF LTE PHYSICAL LAYER by Fahimeh Rezaei A THESIS Presented to the Faculty of The Graduate College at the University of Nebraska In Partial Fulfillment of Requirements For the Degree of Master of Science Major: Telecommunications Engineering Under the Supervision of Professor Hamid.R Sharif-Kashani Lincoln, Nebraska December, 2010 . A COMPREHENSIVE ANALYSIS OF THE LTE
Physical Interface. 3GPP describes LTE radio access technology is described as follows: The multiple access scheme for the LTE physical layer is based on Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiple Access (OFDMA) with a Cyclic Prefix (CP) in the downlink and a Single Carrier Frequency Division Multiple Access (SC-FDMA) with CP in the uplink. SIMULATING THE LONG TERM EVOLUTION PHYSICAL LAYER Christian Mehlfuhr er, Martin Wrulich, Josep Colom Ikuno, Dagmar Bosanska, Markus Rupp Institute of Communications and Radio-Frequency Engineering
LTE video tutorials @RohdeSchwarz presentations provide an excellent introduction to LTE. The presentations are accompanied with an audio narration. Our video tutorials are only available for viewing at our website with an internet connection (no offline option).
A whitepaper on LTE giving a brief introduction to LTE Network element, Radio network, Bearers, QoS, Control plane, user plane and handover procedures. An overview of the LTE physical layer--Part II in Tutorial , LTE physical layer , LTE Telesystem Innovations - This article presents an overview of the LTE physical layer with a focus on essential aspects of the physical layer for FDD mode, which is the dominant mode of operation.
An overview of the LTE physical layer--Part II in Tutorial , LTE physical layer , LTE Telesystem Innovations - This article presents an overview of the LTE physical layer with a focus on essential aspects of the physical layer for FDD mode, which is the dominant mode of operation. LTE improves spectrum efficiency, also defined relative to Release 6. The downlink target is three to four times the The downlink target is three to four times the spectral efficiency of High-Speed Downlink Packet Access (HSDPA) while the uplink target is a two to three time
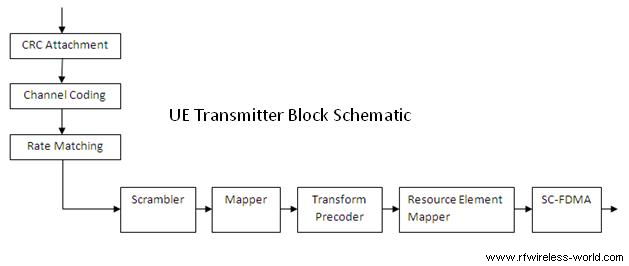
Note: Physical layer aspects for E-MBMS have been taken into account already in 3GPP Release 8, where the support by higher layers has been largely moved to 3GPP Release 9. Let us understand LTE physical layer with example of downlink shared channel(DLВSCH). As shown in the figure As shown in the figure for eNodeB Transmitter upper layer data in the form of transport block is the input to the physical layer.
Below is a logical digram of E-UTRAN Protocol layers with a depiction of data flow through various layers: Packets received by a layer are called Service Data Unit (SDU) while the packet output of a layer is referred to by Protocol Data Unit (PDU). LTE video tutorials @RohdeSchwarz presentations provide an excellent introduction to LTE. The presentations are accompanied with an audio narration.
LTE Physical Layer of subcarriers) below the maximum total output power (assuming all subcarriers are at the same power level).Power Levels . For 10 MHz with 50 RBs there would be 100 RE/symbol that carry the Reference Signal] The RS power per subcarrier and symbol.6 . LTE Physical, Logical and Transport Channels - overview, information, tutorial about the physical, logical, control and transport channels used within 3GPP, 3G LTE and the LTE channel mapping.
LTE Physical Logical and Transport Channels Radio

4G LTE Mobulation Tech Cell Planning & Physical layer. LTE Physical Layer Fundamentals and Test Requirements Fanny Mlinarsky octoScope. December 2009, LTE defines a number of downlink physical channels to carry information blocks received from the MAC and higher layers. These channels are categorized as transport or control channels. These channels are categorized as transport or control channels..
Introduction to the LTE Physical Layer Meetup
Long Term Evolution Protocol Overview NXP Semiconductors. EventHelix.com •telecommunication design •systems engineering •real-time and embedded systems LTE Channel Architecture PHY Physical Channels MAC, "lte physical layer" courses, certification and training IoT Internet of Things Online self paced certification This covers the growth of internet of things encompassing devices for actuation, communication, sensing and processing to develop knowledge and experience in ….
of the LTE physical layer (layer 1 *10) and radio link protocol layer (layer 2 *11) are as follows [1]-[3]. 1) Cell Search Cell search is the process whereby a UE searches for the best cell to connect to. The signal used for cell search is called a Synchronization Signal (SS), and in LTE it is transmitted in the 945 kHz band at the center of the system bandwidth. This allows cell searches to Tutorial outline: I. LTE RAN and Physical layer overview II. LTE RAN security a. Radio jamming b. Protocol-aware radio jamming, smart jamming and very-low-power jamming
LTE-Sim is an open source framework to simulate LTE networks. It encompasses several aspects of LTE networks, including both the Evolved Universal Terrestrial Radio Access (E-UTRAN) and the Evolved Packet System (EPS). Keywords: LTE, location privacy, physical layer identi cation, paging 1 Introduction In all cellular networks, mobile stations (MS) mostly run on battery. To prolong the operational time of the MSs, the network architecture allows them to go into idle mode after being inactive for a certain period of time. In idle mode, the MSs do not sustain a connection with the serving base stations (BS
www.rfwireless-world.com Basics of LTE System Introduction: Third-generation (3G) wireless systems, based on W-CDMA, are now being deployed all over the world. Let us understand LTE physical layer with example of downlink shared channel(DLВSCH). As shown in the figure As shown in the figure for eNodeB Transmitter upper layer data in the form of transport block is the input to the physical layer.
• Only considered is the LTE downlink built between 1 base station (eNodeB) and 1 user equipment (UE). • The focus is mainly on the physical layer and partly on the Our video tutorials are only available for viewing at our website with an internet connection (no offline option).
Overview of the LTE physical layer--Part I in Tutorial , LTE physical layer , LTE Telesystem Innovations - This article presents an overview of the LTE physical layer with a focus on essential aspects of the physical layer for FDD mode, which is the dominant mode of operation. 7 26.01.2002 WCDMA Physical Layer Channelisation (2/3) • In the uplink, it can only separate the physical channels/services of one user because the mobiles are not synchronised in time.
4/06/2017В В· 4G LTE Networks Modulation Technique,Cell Planning,physical layer & Propagation Modeling This blog is about wcdma 3G 4g Lte Telecom/wireless communication & tells evolution in network generation, and how does it works.1Generation to 5 Generation telecom mobile networks. Let us understand LTE physical layer with example of downlink shared channel(DLВSCH). As shown in the figure As shown in the figure for eNodeB Transmitter upper layer data in the form of transport block is the input to the physical layer.
Let us understand LTE physical layer with example of downlink shared channel(DLВSCH). As shown in the figure As shown in the figure for eNodeB Transmitter upper layer data in the form of transport block is the input to the physical layer. Overview of the LTE physical layer--Part I in Tutorial , LTE physical layer , LTE Telesystem Innovations - This article presents an overview of the LTE physical layer with a focus on essential aspects of the physical layer for FDD mode, which is the dominant mode of operation.
19/12/2014В В· This Video Explains LTE technology basics, OFDMA and LTE Frame Structures and types. Importance of SCFDMA (Single Carrier FDMA) and Uplink Frame Structure in LTE. Let us understand LTE physical layer with example of downlink shared channel(DLВSCH). As shown in the figure As shown in the figure for eNodeB Transmitter upper layer data in the form of transport block is the input to the physical layer.
EventHelix.com •telecommunication design •systems engineering •real-time and embedded systems LTE Channel Architecture PHY Physical Channels MAC Physical layer control signals in cellular communications serve the purpose of delivering physical layer control messages in a timely fashion to support cell radio
A whitepaper on LTE giving a brief introduction to LTE Network element, Radio network, Bearers, QoS, Control plane, user plane and handover procedures. Outline of the talk Brief overview of the eNodeB MAC-PHY interface Information sent by the MAC to the PHY oData and control information Concepts of Adaptive Modulation & Coding, BLER &
SIMULATING THE LONG TERM EVOLUTION PHYSICAL LAYER Christian Mehlfuhr er, Martin Wrulich, Josep Colom Ikuno, Dagmar Bosanska, Markus Rupp Institute of Communications and Radio-Frequency Engineering Physical Interface. 3GPP describes LTE radio access technology is described as follows: The multiple access scheme for the LTE physical layer is based on Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiple Access (OFDMA) with a Cyclic Prefix (CP) in the downlink and a Single Carrier Frequency Division Multiple Access (SC-FDMA) with CP in the uplink.
Understanding LTE ShareTechnote. SIMULATING THE LONG TERM EVOLUTION PHYSICAL LAYER Christian Mehlfuhr er, Martin Wrulich, Josep Colom Ikuno, Dagmar Bosanska, Markus Rupp Institute of Communications and Radio-Frequency Engineering, 3glteinfo FREE LTE tutorials and training to get basic and in depth knowledge on various 3GPP Long Term Evolution protocols and procedures. If you are just starting with 3GPP LTE or you have some experience with wireless technologies, our LTE tutorials will help you to understand the next big thing on mobile evolution..
Simulating the Long Term Evolution Physical Layer

Tutorial LTE-Sim Pitkahismi Wimadatu Academia.edu. LTE Physical Layer Fundamentals and Test Requirements Fanny Mlinarsky octoScope. December 2009, www.rfwireless-world.com Basics of LTE System Introduction: Third-generation (3G) wireless systems, based on W-CDMA, are now being deployed all over the world..
THE NS-3 LTE MODULE
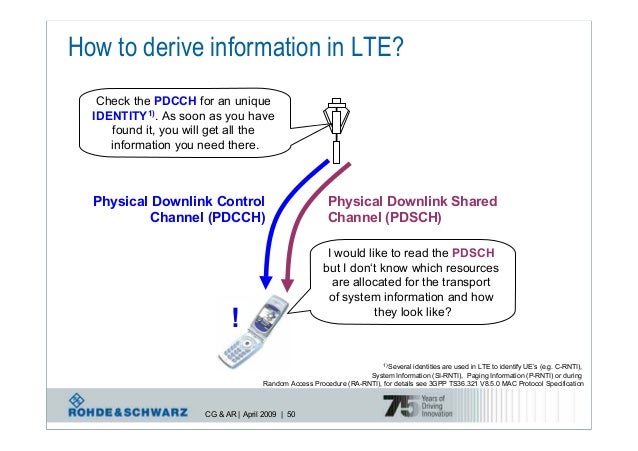
WCDMA Physical Layer (Chapter 6) Aalto. In this paper, the physical layer (PHY) of LTE transceiver is analyzed in downlink and uplink transmissions. Simulations of the physical layer of LTE transceiver are obtained with the use of LTE System Toolbox by Mathworks. Simulation results are presented to show the performance of LTE transceivers in Physical Downlink Shared Channel (PDSCH) and Physical Uplink Shared Channel … • Only considered is the LTE downlink built between 1 base station (eNodeB) and 1 user equipment (UE). • The focus is mainly on the physical layer and partly on the.

LTE tutorial-Page2. This tutorial on LTE covers following topics. Introduction: LTE is the next generation of technology which is backward compatible with cellular technologies such as HSPA,GSM,CDMA etc. LTE means Long Term Evolution.LTE which is known as 4G technology is being specified in Release 8 and 9 of the 3GPP standard. Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. Overview of the 3GPP Long Term Evolution Physical Layer 1 1 Introduction The 3GPP Long Term Evolution (LTE) represents a major advance in cellular technology.
Note: Physical layer aspects for E-MBMS have been taken into account already in 3GPP Release 8, where the support by higher layers has been largely moved to 3GPP Release 9. Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. Overview of the 3GPP Long Term Evolution Physical Layer 1 1 Introduction The 3GPP Long Term Evolution (LTE) represents a major advance in cellular technology.
SC-FDMA & OFDMA in LTE physical layer Murtadha Ali Nsaif Sukar #1 and Maninder Pal *2 #1M.Tech Scholar,Department of Electronics & Communication Engineering, The LTE physical layer is unique because it has asymmetrical modulation and data rates for uplink and downlink. The standard is designed for full-duplex operation, with simultaneous transmission and reception. The radio is optimized for performance on the downlink, because the transmitter at the base station has plenty of power. On the uplink, the radio is optimized more for power consumption
LTE Toolbox™ focuses on the physical layer, which is highlighted in red in the preceding figure. It also supports interfacing with portions of the RLC and MAC layers, which are highlighted in blue. The primary features of the LTE physical layer are OFDM modulation, including the time-frequency structure of the resource blocks, adaptive modulation and coding, hybrid-ARQ, and MIMO. EventHelix.com •telecommunication design •systems engineering •real-time and embedded systems LTE Channel Architecture PHY Physical Channels MAC
LTE Physical Layer. LTE Physical Layer . is 10*log 10 (Total no.RS EPRE and RSRP RS power per subcarrier and symbol Two of the subcarriers in selected symbols in each Resource Block are used for RS from each transmitter.Power Levels .RSRPDiff -85 = TxPowerLevel To Be Set .7 . called Energy per Resource Element (EPRE) in the standard. A COMPREHENSIVE ANALYSIS OF LTE PHYSICAL LAYER by Fahimeh Rezaei A THESIS Presented to the Faculty of The Graduate College at the University of Nebraska In Partial Fulfillment of Requirements For the Degree of Master of Science Major: Telecommunications Engineering Under the Supervision of Professor Hamid.R Sharif-Kashani Lincoln, Nebraska December, 2010 . A COMPREHENSIVE ANALYSIS OF THE LTE
Keywords: LTE, location privacy, physical layer identi cation, paging 1 Introduction In all cellular networks, mobile stations (MS) mostly run on battery. To prolong the operational time of the MSs, the network architecture allows them to go into idle mode after being inactive for a certain period of time. In idle mode, the MSs do not sustain a connection with the serving base stations (BS LTE defines a number of downlink physical channels to carry information blocks received from the MAC and higher layers. These channels are categorized as transport or control channels. These channels are categorized as transport or control channels.
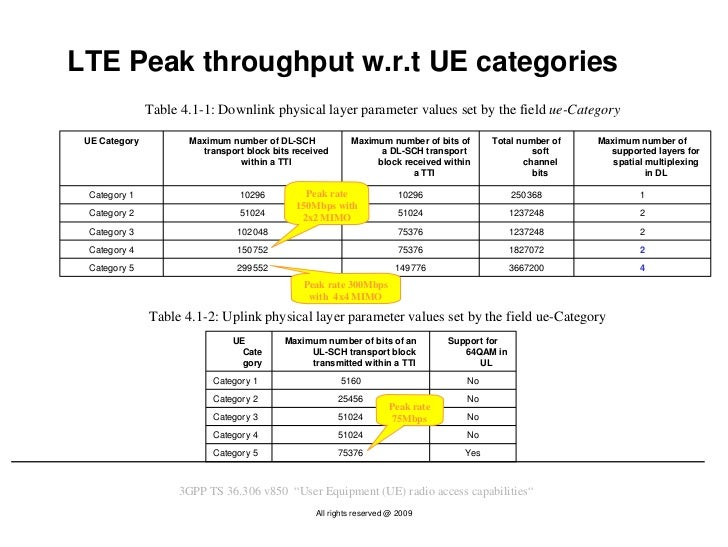
LTE-Sim is an open source framework to simulate LTE networks. It encompasses several aspects of LTE networks, including both the Evolved Universal Terrestrial Radio Access (E-UTRAN) and the Evolved Packet System (EPS). LTE physical layer supports any bandwidth from 1.4 MHz to 20 MHz in steps of 180 kHz (resource block) l Current LTE specification supports a subset of 6 different system bandwidths l All UEs must support the maximum bandwidth of 20 MHz Channel Bandwidth [MHz] Transmission Bandwidth Configuration [RB]
Our video tutorials are only available for viewing at our website with an internet connection (no offline option). 294 IEEE COMMUNICATION SURVEYS & TUTORIALS, VOL. 17, NO. 1, FIRST QUARTER2015 back on commercial LTE networks. The use of LTE in FirstNet is an example of how LTE …
Below is a logical digram of E-UTRAN Protocol layers with a depiction of data flow through various layers: Packets received by a layer are called Service Data Unit (SDU) while the packet output of a layer is referred to by Protocol Data Unit (PDU). Tutorial outline: I. LTE RAN and Physical layer overview II. LTE RAN security a. Radio jamming b. Protocol-aware radio jamming, smart jamming and very-low-power jamming
www.rfwireless-world.com Basics of LTE System Introduction: Third-generation (3G) wireless systems, based on W-CDMA, are now being deployed all over the world. 294 IEEE COMMUNICATION SURVEYS & TUTORIALS, VOL. 17, NO. 1, FIRST QUARTER2015 back on commercial LTE networks. The use of LTE in FirstNet is an example of how LTE …

7 26.01.2002 WCDMA Physical Layer Channelisation (2/3) • In the uplink, it can only separate the physical channels/services of one user because the mobiles are not synchronised in time. An overview of the LTE physical layer--Part II in Tutorial , LTE physical layer , LTE Telesystem Innovations - This article presents an overview of the LTE physical layer with a focus on essential aspects of the physical layer for FDD mode, which is the dominant mode of operation.