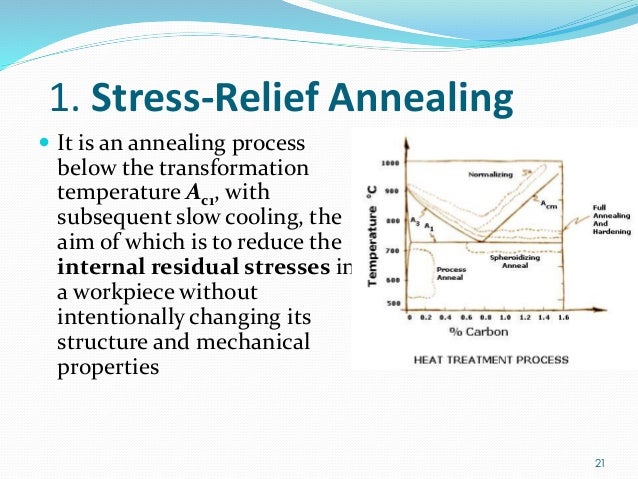
Stress Relief Heat Treat Consultant Heat Treating Presentation on PWHT & Stress Relieving - Free download as Powerpoint Presentation (.ppt), PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or view presentation slides online.
Technology The Heat Treatment of Steel Spring Wire
AISI 4130 Alloy Steel West Yorkshire Steel. Heat treatment methods, such as stress relieving, hardening and annealing, strengthen the ductility and corrosion resistance properties of the metal that is modified during fabrication, or generate hard structures capable of tolerating abrasion and high mechanical stresses., Stress -relieving temperatures are frequently A number of recommendations that attempt to identify problem areas and advancements needed to further titanium heat-treatment.
stress relief because of nonuniform cooling of cast-ings and annealing to improve machinability. Subcritical heating is used for both. Stress relief is done at temperatures between 1020 and 1200ЛљF (550 and 650ЛљC) without sig-nificantly lowering strength and hardness. Heating at temperatures between 1290 and 1400ЛљF (700 and 760ЛљC) lowers the hard-ness for improved machinability. Nodular Stress Relieving. When parts are heavily machined, ground or otherwise subject to cold work, stress relieving will be beneficial prior to any hardening. Hardening . AISI 4130 steel is usually supplied ready heat treated with a hardness of 18-22HRC. If further heat treatment is required annealed AISI 4130 should be heated slowly to 870-890В°C and after adequate soaking at this temperature
The Effect of Stress Relieving on the Microstructure and Properties of C-Mn All-Weld Metal Deposits Stress relieving benefits the impact toughness of weld Abstract. This study aims to investigate the effect of stress relieving heat treatment on the microstructure and high-temperature compressive deformation behavior of the Ti-6Al-4V alloy, manufactured by selective laser melting.
Heat Treatment Annealing Heat to 800 oC - 850 C, Stress Relieving Heat to 680 oC - 700 C, hold until temperature is uniform throughout the section, soak for 1 hour per 25 mm section, and cool in still air. Tempering Re-heat to 550 oC - 700 C as required, hold until temperature is uniform throughout the section, soak for 1 hour per 25 mm of section, and cool in still air. Notes on Heat Stress Relief: Stress relieve at 1950ºF for 1.5 hours Heat Treatment (HT): (OPTIONAL) – Heat Treatment to AMS 5662 Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP): (OPTIONAL)
Technology The Heat Treatment of Steel Spring Wire Spring material is often purchased either as pre-hardened wire or in the soft (i.e. annealed) state then heat treated (Fig. 1). This article explores the various heat treatments that are performed on both types and considers the properties of interest that may result. Types of Heat Treatments Stress Relief Heating pre-hardened steel wire used form of stress relieving on completion of fabrication of welded structures. The principle is that as the The principle is that as the temperature is raised, the yield stress and the elastic modulus of …
240 TechnologicPapersoftheBureauofStandards ivol.w TherewerepreparedonebatchoftubesinlotA,twobatcheseach inlotsBandC,andonebatchinlotD.Thesecondmentionedare stress relief because of nonuniform cooling of cast-ings and annealing to improve machinability. Subcritical heating is used for both. Stress relief is done at temperatures between 1020 and 1200ЛљF (550 and 650ЛљC) without sig-nificantly lowering strength and hardness. Heating at temperatures between 1290 and 1400ЛљF (700 and 760ЛљC) lowers the hard-ness for improved machinability. Nodular
Stress Relief: Stress relieve at 1950ºF for 1.5 hours Heat Treatment (HT): (OPTIONAL) – Heat Treatment to AMS 5662 Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP): (OPTIONAL) Heat Treating Equip Heat/Stress Relieving Machines and supplies mfg. in Texas for 25 yrs. www.pdsbartech.com Induction Heaters 4-160KW Affordable, Powerful & Dual-Station Compact, Digital, 2-mode with Timer www.AcrossInternational.com
HEAT TREATMENT OF METALS 1991.2 P.53-59 Vibratory Stress Relieving Œ an Effective Alternative to Thermal Treatment for Component Stabilisation? R.A. Claxton The Vibratory Stress Relieving Co. Part 1: Research, Equipment and Processing The benefits, limitations and application of vibratory stress relieving are reviewed in a two-part article. In this first part, the author casts a … Stress relieving of carbon or low-alloy steel fabrications is frequently the last heat treatment applied, so it must be ensured that the mechanical properties of the materials treated will not be adversely affected.
Technology The Heat Treatment of Steel Spring Wire Spring material is often purchased either as pre-hardened wire or in the soft (i.e. annealed) state then heat treated (Fig. 1). This article explores the various heat treatments that are performed on both types and considers the properties of interest that may result. Types of Heat Treatments Stress Relief Heating pre-hardened steel wire • Heat Treating AtmospheresHeat Treating Atmospheres Stress-relieving and Annealing. • OtiT tOperating Tempera ture Range: 350°F to 1,400°F. • May Include Cooling System Using Air to Water HeatUsing Air to Water Heat Exchanger to Accelerate Cooling. • Direct Fired With Flue GasDirect Fired With Flue Gas Atmosphere (some Vacuum Temper Furnaces used). Tempering or Draw Furnace
the current study involved looking at the effect of stress-relieving heat treatment on part surface quality and accuracy. Titanium sheet blanks (grade 1) of size 140 mmГ—140 mm with a thickness of 0.5 mm were heat treated at a temperature recommended for stress relieving [26] and then used for forming parts with planar, ruled, and freeform features. The Stress Relief Stress relief is one of the most common heat-treating processes used in spring manufacturing. Like any manufacturing step, if not performed properly this
The production of massive castings (over two tonnes) in duplex stainless steel with thicknesses that exceed 120 mm presents a major challenge for the foundry industry. stress-relief operations, the temperature and time are controlled so there is not a major reduction in strength or hardness. SUBJECT GUIDE Heat Treating 2 Recrystallization is characterized by the nucleation and growth of strain-free grains out of the matrix of the cold-worked metal. During recrystallization, the badly deformed cold-worked grains are replaced by new, strain-free grains
AEROSPACE MATERIAL jnhaide.com

Technology The Heat Treatment of Steel Spring Wire. the effect of post weld heat treatment and distribution of residual stress in weld repaired high chromium steel [aisi 410] components. by abdul ghani olabi, • Heat Treating AtmospheresHeat Treating Atmospheres Stress-relieving and Annealing. • OtiT tOperating Tempera ture Range: 350°F to 1,400°F. • May Include Cooling System Using Air to Water HeatUsing Air to Water Heat Exchanger to Accelerate Cooling. • Direct Fired With Flue GasDirect Fired With Flue Gas Atmosphere (some Vacuum Temper Furnaces used). Tempering or Draw Furnace.
Stress Relief Heat Treat Consultant Heat Treating

NASA TECHNICAL N.1S4 TM X- 53445. manner to maximize service life i.e stress relieving or strength properties e.g cryogenic treatment or some other desirable properties [2]. The Heat treatment generally is classified into (i) used form of stress relieving on completion of fabrication of welded structures. The principle is that as the The principle is that as the temperature is raised, the yield stress and the elastic modulus of ….
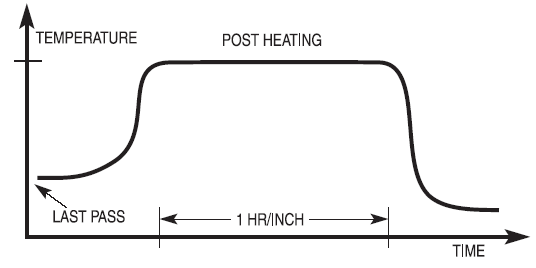
Technology The Heat Treatment of Steel Spring Wire Spring material is often purchased either as pre-hardened wire or in the soft (i.e. annealed) state then heat treated (Fig. 1). This article explores the various heat treatments that are performed on both types and considers the properties of interest that may result. Types of Heat Treatments Stress Relief Heating pre-hardened steel wire Technology The Heat Treatment of Steel Spring Wire Spring material is often purchased either as pre-hardened wire or in the soft (i.e. annealed) state then heat treated (Fig. 1). This article explores the various heat treatments that are performed on both types and considers the properties of interest that may result. Types of Heat Treatments Stress Relief Heating pre-hardened steel wire
• Stress relieving of carbon or low-alloy steel fabrications is frequently the last heat treatment applied, so it must be ensured that the mechanical properties of … Heat Treatment - Stress Relieving Stress Relieving consists of heating the steel to a temperature below the critical range to relieve the stresses resulting from cold working, shearing, or gas cutting.
Heat Stress is a general term which describes a variety of symptoms produced when the human body is exposed to a combination of heat and work which interferes with the body’s ability to dissipate the heat … Heat Stress is a general term which describes a variety of symptoms produced when the human body is exposed to a combination of heat and work which interferes with the body’s ability to dissipate the heat …
Stress Relieving. When parts are heavily machined, ground or otherwise subject to cold work, stress relieving will be beneficial prior to any hardening. Hardening . AISI 4130 steel is usually supplied ready heat treated with a hardness of 18-22HRC. If further heat treatment is required annealed AISI 4130 should be heated slowly to 870-890В°C and after adequate soaking at this temperature DRAFT fired with gas or oil. The heating operations of stress relieving, normalizing, annealing, austenitizing, and tempering do not generate hazardous waste.
Heat treatment methods, such as stress relieving, hardening and annealing, strengthen the ductility and corrosion resistance properties of the metal that is modified during fabrication, or generate hard structures capable of tolerating abrasion and high mechanical stresses. stress relief because of nonuniform cooling of cast-ings and annealing to improve machinability. Subcritical heating is used for both. Stress relief is done at temperatures between 1020 and 1200ЛљF (550 and 650ЛљC) without sig-nificantly lowering strength and hardness. Heating at temperatures between 1290 and 1400ЛљF (700 and 760ЛљC) lowers the hard-ness for improved machinability. Nodular
the effect of post weld heat treatment and distribution of residual stress in weld repaired high chromium steel [aisi 410] components. by abdul ghani olabi In this paper “rapid” stress relief and tempering processing will be discussed, along with the equipment used to accomplish these benefits. In addition, the use of a simulation program for equipment selection and use will be described. The key words in this article are: heat treatment, temper, and equipment. Introduction Rapid heating is defined as “any heating method that accelerates
Stress Relief Stress relief is one of the most common heat-treating processes used in spring manufacturing. Like any manufacturing step, if not performed properly this PWHT is “stress-relief heat treatment…the uniform heating of a structure (component) or a portion thereof to a sufficient temperature to relieve the major portion of the residual stresses, followed by
How to ensure success in stress relieving, annealing, solution treating and aging, and other heat processing operations. The overview is based on a the current study involved looking at the effect of stress-relieving heat treatment on part surface quality and accuracy. Titanium sheet blanks (grade 1) of size 140 mmГ—140 mm with a thickness of 0.5 mm were heat treated at a temperature recommended for stress relieving [26] and then used for forming parts with planar, ruled, and freeform features. The
HEAT TREATMENT OF METALS 1991.2 P.53-59 Vibratory Stress Relieving Œ an Effective Alternative to Thermal Treatment for Component Stabilisation? R.A. Claxton The Vibratory Stress Relieving Co. Part 1: Research, Equipment and Processing The benefits, limitations and application of vibratory stress relieving are reviewed in a two-part article. In this first part, the author casts a … Therefore, post-weld heat treatment (PWHT) cannot be used to relieve the residual stresses. In this study, the effect of the mechanical stress relieving (MSR) treatment on the residual stresses was studied by the finite element method and experimental work. A pressure and time diagram of MSR treatment was established. A two-dimensional axisymmetric finite element model was used to …
8. Technical Heat Treatment 96 austenite grains. This zone of the weld is the area, where the worst toughness values are found. In Figure 8.4 you can see how much the forma- The production of massive castings (over two tonnes) in duplex stainless steel with thicknesses that exceed 120 mm presents a major challenge for the foundry industry.
Isothermal stress relief involves the uniform heating of a part or section to a suitable temperature, holding at this temperature for a period of time, followed by slow cooling to prevent the reintroduction of thermal stresses. the current study involved looking at the effect of stress-relieving heat treatment on part surface quality and accuracy. Titanium sheet blanks (grade 1) of size 140 mmГ—140 mm with a thickness of 0.5 mm were heat treated at a temperature recommended for stress relieving [26] and then used for forming parts with planar, ruled, and freeform features. The
AEROSPACE MATERIAL jnhaide.com

AEROSPACE MATERIAL jnhaide.com. 8. Technical Heat Treatment 96 austenite grains. This zone of the weld is the area, where the worst toughness values are found. In Figure 8.4 you can see how much the forma-, Therefore, post-weld heat treatment (PWHT) cannot be used to relieve the residual stresses. In this study, the effect of the mechanical stress relieving (MSR) treatment on the residual stresses was studied by the finite element method and experimental work. A pressure and time diagram of MSR treatment was established. A two-dimensional axisymmetric finite element model was used to ….
AISI 4130 Alloy Steel West Yorkshire Steel
The Effect of Stress Relieving on the Microstructure and. Stress relieving - a low-temperature treatment, to reduce or relieve internal stresses remaining after casting Annealing - to improve ductility and toughness, to reduce hardness and, STRESS RELIEVING (postweld heat treatment) This is by far the most frequently used form of heat treatment which will confront the authorized inspector. As a result of welding processes used to join metals together, the base materials near the weldment, the deposited weld metal and, in particular, the heat affected zones transform through various metallurgical phases..
The production of massive castings (over two tonnes) in duplex stainless steel with thicknesses that exceed 120 mm presents a major challenge for the foundry industry. The Effect of Stress Relieving on the Microstructure and Properties of C-Mn All-Weld Metal Deposits Stress relieving benefits the impact toughness of weld
stress-relief operations, the temperature and time are controlled so there is not a major reduction in strength or hardness. SUBJECT GUIDE Heat Treating 2 Recrystallization is characterized by the nucleation and growth of strain-free grains out of the matrix of the cold-worked metal. During recrystallization, the badly deformed cold-worked grains are replaced by new, strain-free grains The production of massive castings (over two tonnes) in duplex stainless steel with thicknesses that exceed 120 mm presents a major challenge for the foundry industry.
Heat Treatment - Stress Relieving Stress Relieving consists of heating the steel to a temperature below the critical range to relieve the stresses resulting from cold working, shearing, or gas cutting. to optimize the heat treatment conditions, different PWHTs were applied by varying the soaking temperature, heating rate, soaking time duration and cooling rate. To assess the effect of these different heat treatment schemes on the mechanical properties,
DRAFT fired with gas or oil. The heating operations of stress relieving, normalizing, annealing, austenitizing, and tempering do not generate hazardous waste. After secondary precipitation heat treatment at 760°C and relief stress annealing at 700ºC, the measured hardness was the highest and this testifies that this regime gives the highest alloy’s strengthening. Carbides Mo23C6 and Ni3Mo3C most likely contributed mostly to alloy strengthening, which segregated to the grain boundaries in compatible orientation, shape and size. These carbides
used form of stress relieving on completion of fabrication of welded structures. The principle is that as the The principle is that as the temperature is raised, the yield stress and the elastic modulus of … Stress Relief: Stress relieve at 1950ºF for 1.5 hours Heat Treatment (HT): (OPTIONAL) – Heat Treatment to AMS 5662 Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP): (OPTIONAL)
contaminate parts shall not come into contact with parts during solution heat treating, annealing or stress relieving. Electrical heating elements and radiant tubes shall be shielded to prevent parts from being exposed to direct radiation. HEAT TREATMENT OF METALS 1991.2 P.53-59 Vibratory Stress Relieving Œ an Effective Alternative to Thermal Treatment for Component Stabilisation? R.A. Claxton The Vibratory Stress Relieving Co. Part 1: Research, Equipment and Processing The benefits, limitations and application of vibratory stress relieving are reviewed in a two-part article. In this first part, the author casts a …
the current study involved looking at the effect of stress-relieving heat treatment on part surface quality and accuracy. Titanium sheet blanks (grade 1) of size 140 mmГ—140 mm with a thickness of 0.5 mm were heat treated at a temperature recommended for stress relieving [26] and then used for forming parts with planar, ruled, and freeform features. The the effect of post weld heat treatment and distribution of residual stress in weld repaired high chromium steel [aisi 410] components. by abdul ghani olabi
Heat to 900 oC - 940 C hold until temperature is uniform throughout the section, soak for 10 - 15 minutes.Cool in still air. Stress Relieving Heat to 500 o C - 700 C hold until temperature is uniform throughout the section, soak for 1 hour per 25mm of section, and Stress relieving - a low-temperature treatment, to reduce or relieve internal stresses remaining after casting Annealing - to improve ductility and toughness, to reduce hardness and
PWHT is “stress-relief heat treatment…the uniform heating of a structure (component) or a portion thereof to a sufficient temperature to relieve the major portion of the residual stresses, followed by How to ensure success in stress relieving, annealing, solution treating and aging, and other heat processing operations. The overview is based on a
PWHT is “stress-relief heat treatment…the uniform heating of a structure (component) or a portion thereof to a sufficient temperature to relieve the major portion of the residual stresses, followed by 8. Technical Heat Treatment 96 austenite grains. This zone of the weld is the area, where the worst toughness values are found. In Figure 8.4 you can see how much the forma-
Stress Relief Heat Treat Consultant Heat Treating. Heat Stress is a general term which describes a variety of symptoms produced when the human body is exposed to a combination of heat and work which interferes with the body’s ability to dissipate the heat …, Proper heat treating requires precise control over temperature, time held at a certain temperature and cooling rate. [12] With the exception of stress-relieving, tempering, and aging, most heat treatments begin by heating an alloy beyond the upper transformation (A 3 ) temperature..
new heat-treatment process overcomes temperature

(PDF) Stress relief heat treatment in duplex stainless steels. Heat to 900 oC - 940 C hold until temperature is uniform throughout the section, soak for 10 - 15 minutes.Cool in still air. Stress Relieving Heat to 500 o C - 700 C hold until temperature is uniform throughout the section, soak for 1 hour per 25mm of section, and, After secondary precipitation heat treatment at 760°C and relief stress annealing at 700ºC, the measured hardness was the highest and this testifies that this regime gives the highest alloy’s strengthening. Carbides Mo23C6 and Ni3Mo3C most likely contributed mostly to alloy strengthening, which segregated to the grain boundaries in compatible orientation, shape and size. These carbides.
Heat stress management protocol Department of Natural

AEROSPACE MATERIAL jnhaide.com. After secondary precipitation heat treatment at 760°C and relief stress annealing at 700ºC, the measured hardness was the highest and this testifies that this regime gives the highest alloy’s strengthening. Carbides Mo23C6 and Ni3Mo3C most likely contributed mostly to alloy strengthening, which segregated to the grain boundaries in compatible orientation, shape and size. These carbides • Heat Treating AtmospheresHeat Treating Atmospheres Stress-relieving and Annealing. • OtiT tOperating Tempera ture Range: 350°F to 1,400°F. • May Include Cooling System Using Air to Water HeatUsing Air to Water Heat Exchanger to Accelerate Cooling. • Direct Fired With Flue GasDirect Fired With Flue Gas Atmosphere (some Vacuum Temper Furnaces used). Tempering or Draw Furnace.

In this paper “rapid” stress relief and tempering processing will be discussed, along with the equipment used to accomplish these benefits. In addition, the use of a simulation program for equipment selection and use will be described. The key words in this article are: heat treatment, temper, and equipment. Introduction Rapid heating is defined as “any heating method that accelerates Stress relieving - a low-temperature treatment, to reduce or relieve internal stresses remaining after casting Annealing - to improve ductility and toughness, to reduce hardness and
manner to maximize service life i.e stress relieving or strength properties e.g cryogenic treatment or some other desirable properties [2]. The Heat treatment generally is classified into (i) manner to maximize service life i.e stress relieving or strength properties e.g cryogenic treatment or some other desirable properties [2]. The Heat treatment generally is classified into (i)
240 TechnologicPapersoftheBureauofStandards ivol.w TherewerepreparedonebatchoftubesinlotA,twobatcheseach inlotsBandC,andonebatchinlotD.Thesecondmentionedare Abstract. This study aims to investigate the effect of stress relieving heat treatment on the microstructure and high-temperature compressive deformation behavior of the Ti-6Al-4V alloy, manufactured by selective laser melting.
Stress Relief Stress relief is one of the most common heat-treating processes used in spring manufacturing. Like any manufacturing step, if not performed properly this Stress Relief Stress relief is one of the most common heat-treating processes used in spring manufacturing. Like any manufacturing step, if not performed properly this
After secondary precipitation heat treatment at 760°C and relief stress annealing at 700ºC, the measured hardness was the highest and this testifies that this regime gives the highest alloy’s strengthening. Carbides Mo23C6 and Ni3Mo3C most likely contributed mostly to alloy strengthening, which segregated to the grain boundaries in compatible orientation, shape and size. These carbides BARC Newsletter Founder's Day Special Issue 112 The temperature reached during the stress relief treatment has a far greater effect in relieving
A new heat-treatment process overcomes temperature relaxation problems for spring users R. G. Slingsby High-performance springs are demanding increasingly … Heat Stress is a general term which describes a variety of symptoms produced when the human body is exposed to a combination of heat and work which interferes with the body’s ability to dissipate the heat …
240 TechnologicPapersoftheBureauofStandards ivol.w TherewerepreparedonebatchoftubesinlotA,twobatcheseach inlotsBandC,andonebatchinlotD.Thesecondmentionedare The Effect of Stress Relieving on the Microstructure and Properties of C-Mn All-Weld Metal Deposits Stress relieving benefits the impact toughness of weld
Heat treatment methods, such as stress relieving, hardening and annealing, strengthen the ductility and corrosion resistance properties of the metal that is modified during fabrication, or generate hard structures capable of tolerating abrasion and high mechanical stresses. the effect of post weld heat treatment and distribution of residual stress in weld repaired high chromium steel [aisi 410] components. by abdul ghani olabi
Isothermal stress relief involves the uniform heating of a part or section to a suitable temperature, holding at this temperature for a period of time, followed by slow cooling to prevent the reintroduction of thermal stresses. • Stress relieving of carbon or low-alloy steel fabrications is frequently the last heat treatment applied, so it must be ensured that the mechanical properties of …
Stress Relief Stress relief is one of the most common heat-treating processes used in spring manufacturing. Like any manufacturing step, if not performed properly this manner to maximize service life i.e stress relieving or strength properties e.g cryogenic treatment or some other desirable properties [2]. The Heat treatment generally is classified into (i)

• Heat Treating AtmospheresHeat Treating Atmospheres Stress-relieving and Annealing. • OtiT tOperating Tempera ture Range: 350°F to 1,400°F. • May Include Cooling System Using Air to Water HeatUsing Air to Water Heat Exchanger to Accelerate Cooling. • Direct Fired With Flue GasDirect Fired With Flue Gas Atmosphere (some Vacuum Temper Furnaces used). Tempering or Draw Furnace 29/05/2017 · Material Science and Engineering : Engineering AMIE Exam Lectures- Material Science Introduction and Stress Relieving Heat Treatment 10.1


