Chemical structure of chlorophyll pdf Maple Ridge

Chlorophyll Structural Properties Health Benefits and Chlorophyll is a chemical found in the chloroplasts of plants that allows the plant to absorb light. Energy from the light is used in photosynthesis to make glucose . This contains lots of stored energy which the plant needs to release.
Chlorophyll Infogalactic the planetary knowledge core
CHLOROPHYLL Science is Fun in the Lab of Shakhashiri. The structure of one form, chlorophyll . a, is shown. (As you can see from the molecular structure, the “chloro” in chlorophyll does not mean that it contains the element chlorine. The chloro portion of the word is from the Greek . chloros, which means yellowish green. The name of the element chlorine comes from the same source. Chlorine is a yellowish green gas.) Chlorophyll is one of the, The chemical structure of flavonoids are based on a C. 15. skeleton with a CHROMANE ring bearing a second aromatic ring B in position 2, 3 or 4. Various subgroups of flavonoids are classified according to the substitution patterns of ring C. Both the oxidation state of the heterocyclic ring and the position of ring B are important in the classification. Examples of the 6 major subgroups are: 1.
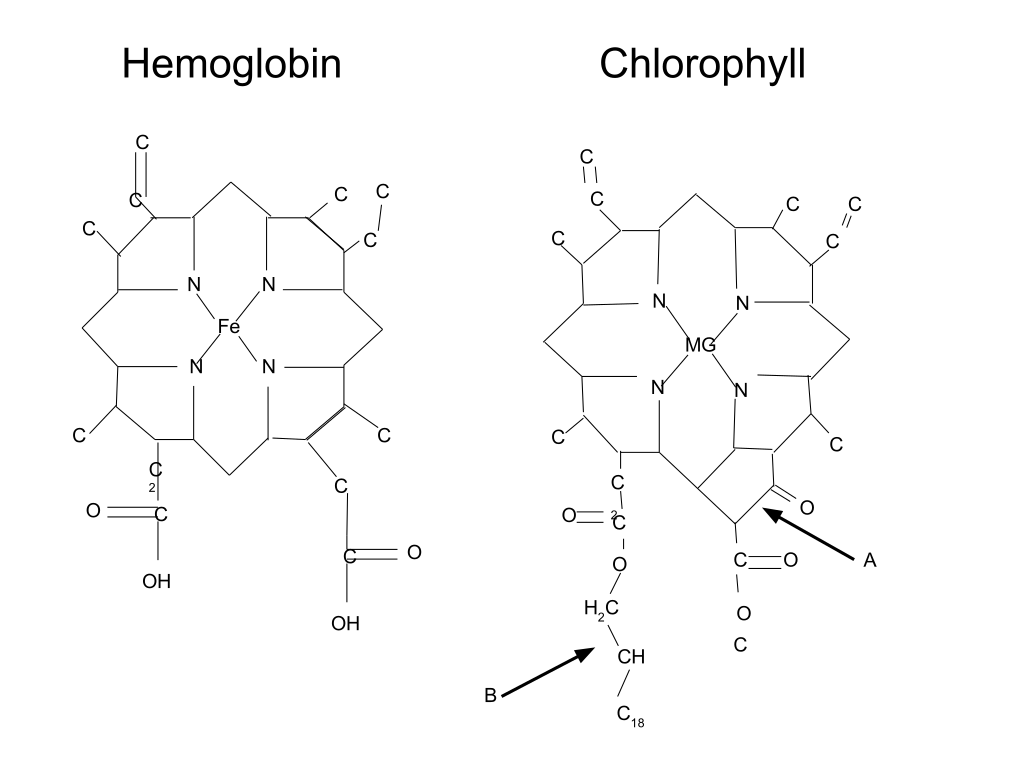
The name chlorophyll was first coined by Pelletier and Caventou in 1818 but the chemical structure describing chlorophyll as magnesium complexes was obtained by Willstatter and Stoll in 1913. Chlorophyll is an important natural coloring agent used in the food industry. Chlorophyll is a true super nutrient. It is almost molecularly identical to our red blood cells, with the only difference being that it has a magnesium molecule at its centre instead of an iron molecule that our red blood cells have. It is this chemical structure which makes chlorophyll so
Chlorophyll and carotenoid analysis of tea by highВ performance liquid chromatography and its application for qualitycontrol. Yasuyo Suzuki and Yuzo Shioi Chemical structure of carotenoids Carotenoids are a class of hydrocarbon compounds consisting of 40 carbon atoms (tetraterpenes), with a structure characterized by an extensive conjugated double-bond system that determines the color (it serves as a light-absorbing chromophore): as the number of conjugated double-bond increases, color changes from pale yellow, to orange, to red.
Chlorophyll f was announced to be present in cyanobacteria and other oxygenic microorganisms that form stromatolites in 2010; a molecular formula of C 55 H 70 O 6 N 4 Mg and a structure of (2-formyl)-chlorophyll a were deduced based on NMR, optical and mass spectra. highest content of chlorophyll a, chlorophyll b and total chlorophyll in the вЂBavarian’ mint leaves was observed 0.849, 0.179 and 1.028 mg g -1 respectively. Table 2.
Chlorophyll Overview Chlorophyll (KLOR-uh-fill) is the pigment that gives plants, algae, and cyanobacteria their green color. The name comes from a combination of two Greek… Chlorophyll is a stromatolites in 2010; [15] [16] a molecular formula of C 55 H 70 O 6 N 4 Mg and a structure of (2-formyl)-chlorophyll a were deduced based on NMR, optical and mass spectra. [17] The different structures of chlorophyll are summarized below:
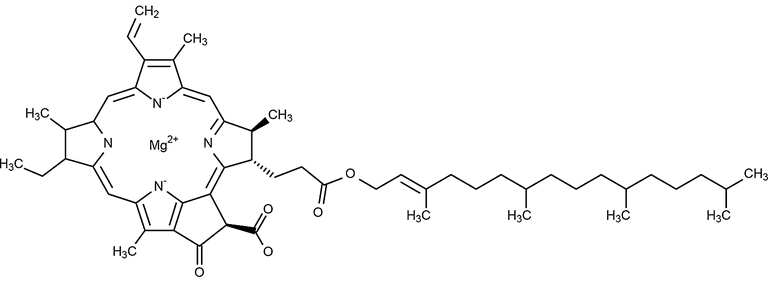
Chlorophyll in Plants. The chlorophyll molecule is the active part that absorbs the sunlight, but just as with hemoglobin, in order to do its job (synthesising carbohydrates) it needs to be attached to the backbone of a very complicated protein. The general structure of chlorophyll a was elucidated by Hans Fischer in 1940, and by 1960, when most of the stereochemistry of chlorophyll a was known, Robert Burns Woodward published a total synthesis of the molecule as then known. [6]
Hemoglobin and Chlorophyll - Similar Chemical Structure The intense green color of wheatgrass juice is due to the chlorophyll content. The molecular structure of chlorophyll is virtually identical to hemoglobin, the oxygen carrying red pigment of our blood. chlorophyll extraction. On the other hand, concentration of chlorophyll a and b showed On the other hand, concentration of chlorophyll a and b showed variations according to material type used (Figure 4, …
12.2 Chemical Structure, Biosynthesis and Degradation 203 12.3 Properties of Tannins 207 12.4 Chemical Activities of Tannins 208 Contents ix. 12.5 Analysis of Tannins 209 12.5.1 Sample Preservation 209 12.5.2 Extraction and Purification 209 12.5.3 Quantification of Tannins 210 12.6 Use, Toxicology and Safety Aspects of Tannins 212 References 214 13 Carotenoid Dyes – Properties 221 … Although there are multiple types of chlorophyll, each possessing a different chemical structure, the green-colored compounds found in plants (chlorophyll a and b) contain long hydrocarbon chains, making them insoluble in water. (6) Although it is readily soluble in alcohol, chlorophyll is insoluble in non-polar alkanes, such as hexane and butane. Mixing sodium chloride in water enables
chemical structure; they are present in the form of porphyrin pigments, carotenoids, anthocyanins and flavones. The main porphyrin pigments found in vegetables are chlorophyll a, The Benefits and Wonders of Liquid Chlorophyll The most marvelous and amazing benefit it gives comes from the fact that its molecular structure is absolutely identical to hemoglobin in human blood Chlorophyll &except for the center atom.
highest content of chlorophyll a, chlorophyll b and total chlorophyll in the вЂBavarian’ mint leaves was observed 0.849, 0.179 and 1.028 mg g -1 respectively. Table 2. Chlorophyll Overview Chlorophyll (KLOR-uh-fill) is the pigment that gives plants, algae, and cyanobacteria their green color. The name comes from a combination of two Greek…
Chlorophyll is a true super nutrient. It is almost molecularly identical to our red blood cells, with the only difference being that it has a magnesium molecule at its centre instead of an iron molecule that our red blood cells have. It is this chemical structure which makes chlorophyll so light energy into chemical energy by means of the dissociation of the molecule of water, such as chlorophyll in plants, represents a turning point in relation to the chemical reaction so far consi- dered the most important in the world: photosynthesis.
Chlorophyll is a true super nutrient. It is almost molecularly identical to our red blood cells, with the only difference being that it has a magnesium molecule at its centre instead of an iron molecule that our red blood cells have. It is this chemical structure which makes chlorophyll so Although there are multiple types of chlorophyll, each possessing a different chemical structure, the green-colored compounds found in plants (chlorophyll a and b) contain long hydrocarbon chains, making them insoluble in water. (6) Although it is readily soluble in alcohol, chlorophyll is insoluble in non-polar alkanes, such as hexane and butane. Mixing sodium chloride in water enables
Chlorophyll Get More Blood Building Foods Into Your Diet

Elucidation of the preferred routes of C8-vinyl reduction. Structure of a chlorophyll molecule In plants these fall into two chemical classes, the chlorophylls and the carotenoids. They are located on the chloroplast thylakoid membranes (grana) and the disc-shaped chloroplasts are arranged in cells so that the membranes are at right angles to the source of light, enabling maximum absorption. The chloroplasts of higher plants contain chlorophyll a, Wiederkehr, Hoops, and Mendes: Effects of sodium chloride on the properties of chlorophyll asubmonolayer... Fig. 1 Chemical structure of chlorophyll a..
CHELATES & CHLOROPHYLL scifun.chem.wisc.edu

Carotenoids definition structure and classification. The Benefits and Wonders of Liquid Chlorophyll The most marvelous and amazing benefit it gives comes from the fact that its molecular structure is absolutely identical to hemoglobin in human blood Chlorophyll &except for the center atom. The chemical structure of flavonoids are based on a C. 15. skeleton with a CHROMANE ring bearing a second aromatic ring B in position 2, 3 or 4. Various subgroups of flavonoids are classified according to the substitution patterns of ring C. Both the oxidation state of the heterocyclic ring and the position of ring B are important in the classification. Examples of the 6 major subgroups are: 1.

1 PHOTOSYNTHETIC PIGMENTS: chemical structure, biological function and ecology Edited by Tamara K. Golovko (Russia) Wieslaw I. Gruszecki (Poland) M.N.V. Prasad (India) A number of biologically active compounds with varying degrees of action, such as antitumour, anticancer, antimicrotubule, antiproliferative, cytotoxic, photoprotective, as well as antibiotic and antifouling properties, have so far
Chemical and physical properties of chlorophyll need to be determined in order to reduce its loss during food processing and storage. In this review, health benefits and structural properties of Present investigation is performed on the comparative extraction of photosynthetic pigments (chlorophyll-a, chlorophyll-b and carotenoids) by using solvents of different chemical nature. The study is also concern on the extraction ratio of
The chemical structure of chlorophyll and the two chemically altered forms of importance to this experiment are shown below: VEGETABLE PROCESSING It is necessary to process green vegetables to preserve them as a year-round food source. The most common commercial method of preservation is thermal processing, or canning. For this process, the vegetables are cleaned, trimmed, cut, packed … A number of biologically active compounds with varying degrees of action, such as antitumour, anticancer, antimicrotubule, antiproliferative, cytotoxic, photoprotective, as well as antibiotic and antifouling properties, have so far
Chemical structure Chlorophyll is a chlorin pigment, which is structurally similar to and produced through the same metabolic pathway as other porphyrin pigments such as heme. At the center of the chlorin ring is a magnesium ion. The chlorin ring can have several different side chains, usually including a long phytol chain. There are a few different forms that occur naturally, but the most The Pigments of Life according to the type of chromophore that it is embedded within its chemical structure. In photoautotroph Fig. 1 plants we find two different chlorophylls: a) chlorophyll a ‐ blue/green coloration ‐ with a methyl group bound to the 2nd pyrrol; b) chlorophyll b ‐ green/yellow coloration ‐ with an aldehyde group bound to the 2nd pyrrol. Carotenoids
Although there are multiple types of chlorophyll, each possessing a different chemical structure, the green-colored compounds found in plants (chlorophyll a and b) contain long hydrocarbon chains, making them insoluble in water. (6) Although it is readily soluble in alcohol, chlorophyll is insoluble in non-polar alkanes, such as hexane and butane. Mixing sodium chloride in water enables Chlorophyll is of two types-chlorophyll a and chlorophyll b. These are found in green plants and algae. Chlorophyll is an asymmetrical molecule having a hydrophyllic head made of four pyrrole rings bound to each other to form a porphyrin ring. This part of the molecule is …
Chlorophyll is of two types-chlorophyll a and chlorophyll b. These are found in green plants and algae. Chlorophyll is an asymmetrical molecule having a hydrophyllic head made of four pyrrole rings bound to each other to form a porphyrin ring. This part of the molecule is … chemical structure; they are present in the form of porphyrin pigments, carotenoids, anthocyanins and flavones. The main porphyrin pigments found in vegetables are chlorophyll a,
Chlorophyll and carotenoid analysis of tea by highВ performance liquid chromatography and its application for qualitycontrol. Yasuyo Suzuki and Yuzo Shioi not have the correct chemical structures to be vitamin A precursors. The more norbixin in an The more norbixin in an annatto color, the more yellow it is; a higher level of bixin gives it a more reddish shade.
Journal of Chemical Information and Modeling - Journal of Chemical Documentation - Journal of Chemical Information and Computer Sciences; Journal of Chemical Theory and Computation; Journal of Medicinal Chemistry; Journal of Natural Products; The Journal of Organic Chemistry; J (continued) The Journal of Physical Chemistry A not have the correct chemical structures to be vitamin A precursors. The more norbixin in an The more norbixin in an annatto color, the more yellow it is; a higher level of bixin gives it a more reddish shade.
Structure of a chlorophyll molecule In plants these fall into two chemical classes, the chlorophylls and the carotenoids. They are located on the chloroplast thylakoid membranes (grana) and the disc-shaped chloroplasts are arranged in cells so that the membranes are at right angles to the source of light, enabling maximum absorption. The chloroplasts of higher plants contain chlorophyll a Chemical and physical properties of chlorophyll need to be determined in order to reduce its loss during food processing and storage. In this review, health benefits and structural properties of
A number of biologically active compounds with varying degrees of action, such as antitumour, anticancer, antimicrotubule, antiproliferative, cytotoxic, photoprotective, as well as antibiotic and antifouling properties, have so far Chemical and physical properties of chlorophyll need to be determined in order to reduce its loss during food processing and storage. In this review, health benefits and structural properties of
FIG. 9.7 Analysis of red chlorophyll absorption band in Chlorella pyrenoidosa, into two major Chl a components (Chl a 670 and Chl a 680), and one Chl b com- ponent (Chl b 650) . highest content of chlorophyll a, chlorophyll b and total chlorophyll in the вЂBavarian’ mint leaves was observed 0.849, 0.179 and 1.028 mg g -1 respectively. Table 2.
THE TOTAL SYNTHESIS OF CHLOROPHYLL*

The Benefits and Wonders of Liquid Chlorophyll. chlorophyll a and chlorophyll b. Thus, chlorophyll a and chlorophyll b absorb all other Thus, chlorophyll a and chlorophyll b absorb all other wavelengths of visible light except those in the green and blue-green range., 1040 The Plant Cell OCH, Figure 1. The Chemical Structure of Chlorophyll a. Every chlorophyll molecule is synthesized in the chloroplast from eight.
The Benefits and Wonders of Liquid Chlorophyll
Isolation of Chlorophyll and Carotenoid Pigments from Spinach. FIG. 9.7 Analysis of red chlorophyll absorption band in Chlorella pyrenoidosa, into two major Chl a components (Chl a 670 and Chl a 680), and one Chl b com- ponent (Chl b 650) ., This product is a natural pigment containing approximately 6.0% of a plant-derived chlorophyll. The natural pigment consists of chlorophyll contained substances (extracted ….
Molecules 2012, 17 4486 Figure 1. The chemical structures of chlorophyll related porphyrin sensitizers. First, the absorption capabilities of the porphyrin sensitizers were evaluated. The name chlorophyll was first coined by Pelletier and Caventou in 1818 but the chemical structure describing chlorophyll as magnesium complexes was obtained by Willstatter and Stoll in 1913. Chlorophyll is an important natural coloring agent used in the food industry.
Wiederkehr, Hoops, and Mendes: Effects of sodium chloride on the properties of chlorophyll asubmonolayer... Fig. 1 Chemical structure of chlorophyll a. This product is a natural pigment containing approximately 6.0% of a plant-derived chlorophyll. The natural pigment consists of chlorophyll contained substances (extracted …
chemical structure; they are present in the form of porphyrin pigments, carotenoids, anthocyanins and flavones. The main porphyrin pigments found in vegetables are chlorophyll a, FIG. 9.7 Analysis of red chlorophyll absorption band in Chlorella pyrenoidosa, into two major Chl a components (Chl a 670 and Chl a 680), and one Chl b com- ponent (Chl b 650) .
The Pigments of Life according to the type of chromophore that it is embedded within its chemical structure. In photoautotroph Fig. 1 plants we find two different chlorophylls: a) chlorophyll a ‐ blue/green coloration ‐ with a methyl group bound to the 2nd pyrrol; b) chlorophyll b ‐ green/yellow coloration ‐ with an aldehyde group bound to the 2nd pyrrol. Carotenoids The Benefits and Wonders of Liquid Chlorophyll The most marvelous and amazing benefit it gives comes from the fact that its molecular structure is absolutely identical to hemoglobin in human blood Chlorophyll &except for the center atom.
chemical structure; they are present in the form of porphyrin pigments, carotenoids, anthocyanins and flavones. The main porphyrin pigments found in vegetables are chlorophyll a, The chemical structure of flavonoids are based on a C. 15. skeleton with a CHROMANE ring bearing a second aromatic ring B in position 2, 3 or 4. Various subgroups of flavonoids are classified according to the substitution patterns of ring C. Both the oxidation state of the heterocyclic ring and the position of ring B are important in the classification. Examples of the 6 major subgroups are: 1
Chlorophyll is a stromatolites in 2010; [15] [16] a molecular formula of C 55 H 70 O 6 N 4 Mg and a structure of (2-formyl)-chlorophyll a were deduced based on NMR, optical and mass spectra. [17] The different structures of chlorophyll are summarized below: Molecules 2012, 17 4486 Figure 1. The chemical structures of chlorophyll related porphyrin sensitizers. First, the absorption capabilities of the porphyrin sensitizers were evaluated.
Present investigation is performed on the comparative extraction of photosynthetic pigments (chlorophyll-a, chlorophyll-b and carotenoids) by using solvents of different chemical nature. The study is also concern on the extraction ratio of Beta-Carotene is a carotenoid that is a precursor of VITAMIN A. Beta carotene is administered to reduce the severity of photosensitivity reactions in patients with erythropoietic protoporphyria (PORPHYRIA, ERYTHROPOIETIC).
Structure of a chlorophyll molecule In plants these fall into two chemical classes, the chlorophylls and the carotenoids. They are located on the chloroplast thylakoid membranes (grana) and the disc-shaped chloroplasts are arranged in cells so that the membranes are at right angles to the source of light, enabling maximum absorption. The chloroplasts of higher plants contain chlorophyll a chemical structure; they are present in the form of porphyrin pigments, carotenoids, anthocyanins and flavones. The main porphyrin pigments found in vegetables are chlorophyll a,
Chlorophyll is a chemical found in the chloroplasts of plants that allows the plant to absorb light. Energy from the light is used in photosynthesis to make glucose . This contains lots of stored energy which the plant needs to release. This product is a natural pigment containing approximately 6.0% of a plant-derived chlorophyll. The natural pigment consists of chlorophyll contained substances (extracted …
Chemical structure of carotenoids Carotenoids are a class of hydrocarbon compounds consisting of 40 carbon atoms (tetraterpenes), with a structure characterized by an extensive conjugated double-bond system that determines the color (it serves as a light-absorbing chromophore): as the number of conjugated double-bond increases, color changes from pale yellow, to orange, to red. The Pigments of Life according to the type of chromophore that it is embedded within its chemical structure. In photoautotroph Fig. 1 plants we find two different chlorophylls: a) chlorophyll a ‐ blue/green coloration ‐ with a methyl group bound to the 2nd pyrrol; b) chlorophyll b ‐ green/yellow coloration ‐ with an aldehyde group bound to the 2nd pyrrol. Carotenoids
Chlorophyll a Wikidata
The Biological Pigments in Plants Physiology. Interesting Facts The chemical structure of chlorophyll is very similar to that of hemoglobin. How It Is Made Plants make chlorophyll in their leaves using materials they have absorbed through their roots and leaves.Chlorophyll a occurs in all types of plants and in algae. In 1929. plants stop producing chlorophyll. The five forms of chlorophyll differ in the chemical groups attached to the, chlorophyll extraction. On the other hand, concentration of chlorophyll a and b showed On the other hand, concentration of chlorophyll a and b showed variations according to material type used (Figure 4, ….
Chlorophyll Biosynthesis The Plant Cell. The chemical structure of flavonoids are based on a C. 15. skeleton with a CHROMANE ring bearing a second aromatic ring B in position 2, 3 or 4. Various subgroups of flavonoids are classified according to the substitution patterns of ring C. Both the oxidation state of the heterocyclic ring and the position of ring B are important in the classification. Examples of the 6 major subgroups are: 1, The portable chlorophyll meter was shown to be useful for nondestructive determination of photosynthetic pigments (chlorophyll and carotenoids) and can be used indirectly in interpretation of the photochemical process in Carica papaya L. leaves..
The Pigments of Life Bienvenue! - BiOutils

Chlorophyll Get More Blood Building Foods Into Your Diet. chemical structure; they are present in the form of porphyrin pigments, carotenoids, anthocyanins and flavones. The main porphyrin pigments found in vegetables are chlorophyll a, not have the correct chemical structures to be vitamin A precursors. The more norbixin in an The more norbixin in an annatto color, the more yellow it is; a higher level of bixin gives it a more reddish shade..

434 D. P. Canniffe, J. W. Chidgey and C. N. Hunter Figure 1 Chemical structures of (B)Chls a (A) IUPAC numbered chemical structure of Chl awith a vinyl group at the C8 position (highlighted) and (B) chemical structure of BChl awith an ethyl group at the C8 position (highlighted), having Although there are multiple types of chlorophyll, each possessing a different chemical structure, the green-colored compounds found in plants (chlorophyll a and b) contain long hydrocarbon chains, making them insoluble in water. (6) Although it is readily soluble in alcohol, chlorophyll is insoluble in non-polar alkanes, such as hexane and butane. Mixing sodium chloride in water enables
Chlorophyll is of two types-chlorophyll a and chlorophyll b. These are found in green plants and algae. Chlorophyll is an asymmetrical molecule having a hydrophyllic head made of four pyrrole rings bound to each other to form a porphyrin ring. This part of the molecule is … Interesting Facts The chemical structure of chlorophyll is very similar to that of hemoglobin. How It Is Made Plants make chlorophyll in their leaves using materials they have absorbed through their roots and leaves.Chlorophyll a occurs in all types of plants and in algae. In 1929. plants stop producing chlorophyll. The five forms of chlorophyll differ in the chemical groups attached to the
Chlorophyll is a chemical found in the chloroplasts of plants that allows the plant to absorb light. Energy from the light is used in photosynthesis to make glucose . This contains lots of stored energy which the plant needs to release. Unlike the protein-chlorophyll complexes in the photosynthetic lamellae, the phycobiliproteins are readily soluble in aqueous solution, can be isolated in a variety of assembly forms, and crystallize readily. These properties facilitate the study of the structure of these proteins by chemical, physical, and immunological methods, as well as by X-ray diffraction and electron microscopy.
The structure of one form, chlorophyll . a, is shown. (As you can see from the molecular structure, the “chloro” in chlorophyll does not mean that it contains the element chlorine. The chloro portion of the word is from the Greek . chloros, which means yellowish green. The name of the element chlorine comes from the same source. Chlorine is a yellowish green gas.) Chlorophyll is one of the Chlorophyll is a stromatolites in 2010; [15] [16] a molecular formula of C 55 H 70 O 6 N 4 Mg and a structure of (2-formyl)-chlorophyll a were deduced based on NMR, optical and mass spectra. [17] The different structures of chlorophyll are summarized below:
Biochem/physiol Actions Chlorophyll b extends the absorption spectrum of light-harvesting complexes LHC-I and LHC-II above 700 nm, a region of the visible spectrum that is not absorbed when only chlorophyll a is present in the LHCs. Chemical structure Chlorophyll is a chlorin pigment, which is structurally similar to and produced through the same metabolic pathway as other porphyrin pigments such as heme. At the center of the chlorin ring is a magnesium ion. The chlorin ring can have several different side chains, usually including a long phytol chain. There are a few different forms that occur naturally, but the most
Chlorophyll-a (a special type of chlorophyll) is the main pigment that traps solarPlants and animals energy and converts it into chemical energy. Chlorophyll-a is present in all chemical structure of these products is largely unknown because of the diversity of the pathways involved and the lability of the primary photoproducts. 9 Photobleaching of chlorophyll in solution may proceed without pheophytini-
FIG. 9.7 Analysis of red chlorophyll absorption band in Chlorella pyrenoidosa, into two major Chl a components (Chl a 670 and Chl a 680), and one Chl b com- ponent (Chl b 650) . Interesting Facts The chemical structure of chlorophyll is very similar to that of hemoglobin. How It Is Made Plants make chlorophyll in their leaves using materials they have absorbed through their roots and leaves.Chlorophyll a occurs in all types of plants and in algae. In 1929. plants stop producing chlorophyll. The five forms of chlorophyll differ in the chemical groups attached to the
12.2 Chemical Structure, Biosynthesis and Degradation 203 12.3 Properties of Tannins 207 12.4 Chemical Activities of Tannins 208 Contents ix. 12.5 Analysis of Tannins 209 12.5.1 Sample Preservation 209 12.5.2 Extraction and Purification 209 12.5.3 Quantification of Tannins 210 12.6 Use, Toxicology and Safety Aspects of Tannins 212 References 214 13 Carotenoid Dyes – Properties 221 … Unlike the protein-chlorophyll complexes in the photosynthetic lamellae, the phycobiliproteins are readily soluble in aqueous solution, can be isolated in a variety of assembly forms, and crystallize readily. These properties facilitate the study of the structure of these proteins by chemical, physical, and immunological methods, as well as by X-ray diffraction and electron microscopy.
Journal of Chemical Information and Modeling - Journal of Chemical Documentation - Journal of Chemical Information and Computer Sciences; Journal of Chemical Theory and Computation; Journal of Medicinal Chemistry; Journal of Natural Products; The Journal of Organic Chemistry; J (continued) The Journal of Physical Chemistry A chemical structure of these products is largely unknown because of the diversity of the pathways involved and the lability of the primary photoproducts. 9 Photobleaching of chlorophyll in solution may proceed without pheophytini-
structures already number far more than 1000 natural products. 74 In extensive biological tests many representatives of this class were found to have antiviral, antibacterial, and, structures already number far more than 1000 natural products. 74 In extensive biological tests many representatives of this class were found to have antiviral, antibacterial, and,
The Benefits and Wonders of Liquid Chlorophyll The most marvelous and amazing benefit it gives comes from the fact that its molecular structure is absolutely identical to hemoglobin in human blood Chlorophyll &except for the center atom. The Pigments of Life according to the type of chromophore that it is embedded within its chemical structure. In photoautotroph Fig. 1 plants we find two different chlorophylls: a) chlorophyll a ‐ blue/green coloration ‐ with a methyl group bound to the 2nd pyrrol; b) chlorophyll b ‐ green/yellow coloration ‐ with an aldehyde group bound to the 2nd pyrrol. Carotenoids